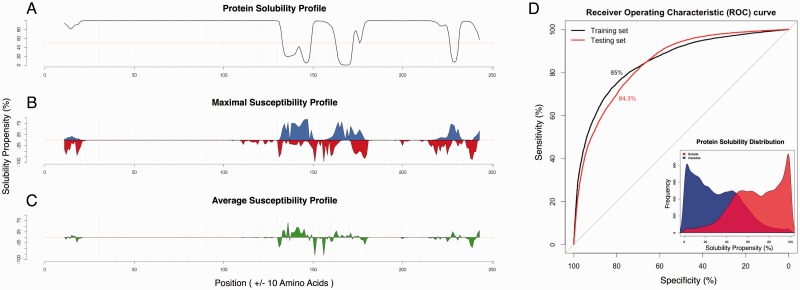
Fig. 1.
Human Prion Solubility and ccSOL Performances. (A) Starting from the N-terminus, ccSOL computes the solubility profile using a sliding window moved toward the C-terminus. ccSOL identifies the fragment 130–170 as the most insoluble within the C-terminus of human PrP (region 231–253 is not present in the mature form of the protein). (B, C) Maximal and average susceptibility upon single-point mutation. (D) We trained on the Target Track set (AUROC = 85.5%) and tested on E.coli [AUROC = 93.3%; (Niwa et al., 2009)], SOLpro [AUROC = 85.7%; (Magnan et al., 2009)] and PROSO II [AUROC = 82.9%; (Smialowski et al., 2012)] proteins. Inset: overall score distribution for soluble (red) and insoluble (blue) proteins