Figure 1.
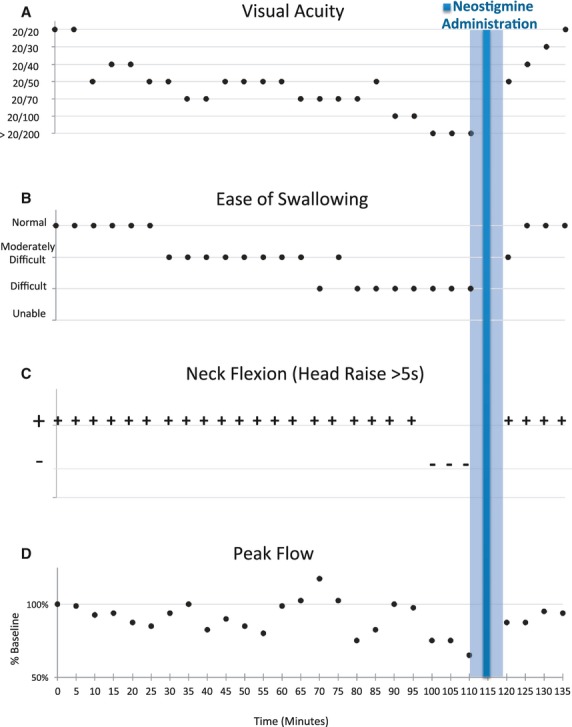
Clinical measures of muscle function are represented as a function of time with baseline measurements at Time 0 at the start of mivacurium infusion and ending at 135 min with the termination of the mivacurium infusion. Intranasal neostigmine was administered at 115 min after establishing the presence of clinically significant neuromuscular impairment and electrophysiologically stable neuromuscular blockade. Stable impairment and the constant mivacurium infusion rate allowed for pre- and postneostigmine administration comparisons as illustrated by: A) progressive loss and recovery of visual acuity and B) ease of swallowing were affected before late loss of C) neck flexion, and finally, D) decrement in peak flow, followed by almost complete recovery prior to terminating mivacurium after 135 min.
