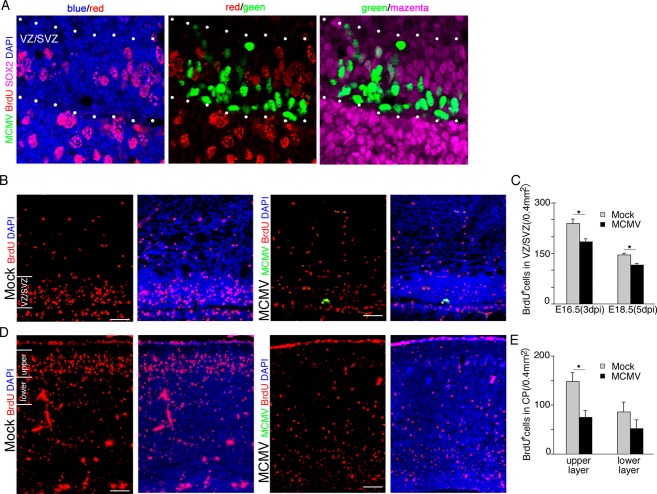
Figure 7.
MCMV infection inhibits the proliferation of NSPCs via both direct and indirect mechanisms. (A–C) Mock- and MCMV-infected pregnant mice were injected with BrdU at 3 and 5 dpi, and the brains of their fetuses were removed at 3 h after the injection. (A) Detection of MCMV-IE1 Ag (green), BrdU (red), and SOX2 (magenta) by immunofluorescence staining of section of the MCMV-infected fetal cerebrum at 3 dpi. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). At 3 dpi, BrdU incorporation is completely inhibited in MCMV-infected NSPCs of the VZ/SVZ between dotted lines. Scale bar = 20 μm. (B) The number of BrdU+ NSPCs adjacent to MCMV infectious focus in the MCMV-infected cerebrum (right) decreased in comparison with that in the mock-infected cerebrum (left) at 5 dpi (E18.5). Scale bar = 50 μm. (C) The number of BrdU+ cells in the uninfected areas of the VZ/SVZ in the mock- or MCMV-infected cerebrum at 3 or 5 dpi. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of three fetuses. *P < 0.05 compared with mock-infected fetuses. (D–E) Mock- and MCMV-infected pregnant mice were injected with BrdU at 24 h after infection and then the fetuses were removed at 96 h after BrdU injection (E18.5, 5 dpi). (D) The number of BrdU+ cells in the cortical plate of the MCMV-infected cerebrum (right) decreased in comparison with the mock-infected cerebrum (left). Scale bar = 50 μm. (E) The number of BrdU+ cells in the upper layer or the lower layer of the cortical plate in the mock-infected or MCMV-infected cerebrum at 5 dpi. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of three fetuses. *P < 0.05 compared with mock-infected fetuses. MCMV, murine cytomegalovirus; NSPC, neural stem/progenitor cells; VZ, ventricular zone; SVZ, subventricular zone.