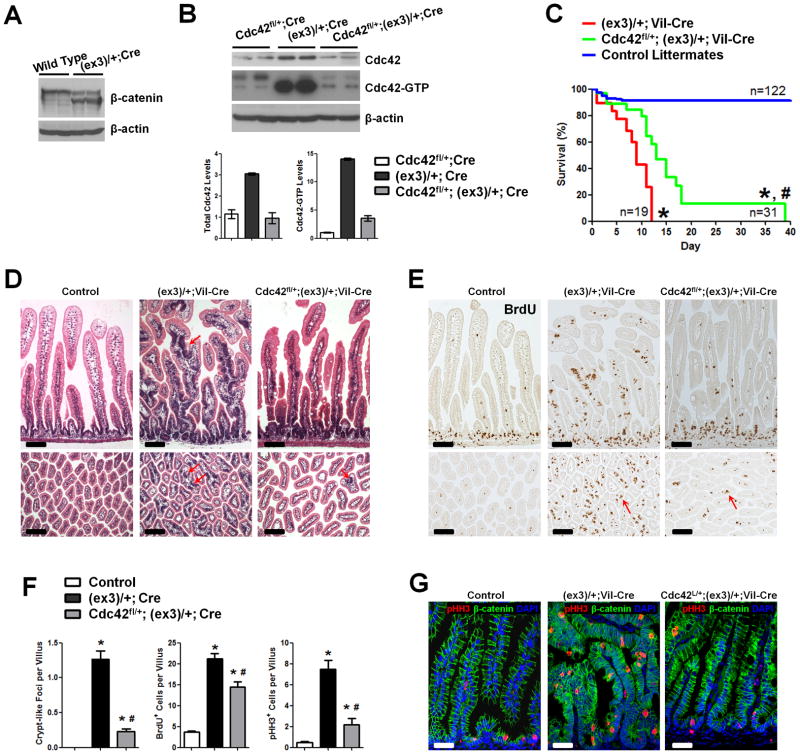
Figure 3. Cdc42 reduction attenuates tumorigenesis in β-catenin stable mutant intestines.
(A) Western blots for β-catenin identified truncated protein in Catnblox(ex3)/+;Vil-Cre intestines.
(B) Western blots for showed 3- and 14-fold increases in the total and active Cdc42 levels in Catnblox(ex3)/+;Vil-Cre mouse intestines, comparing to littermate Cdc42fl/+;Vil-Cre mice.
(C) Cdc42 haploinsufficiency extended median survival time for 4 days (p<0.001).
(D) Cdc42 reduction reduced crypt-like foci (arrows) throughout the epithelia. Histological analyses were done on mouse small intestines from postnatal day 7 mice with indicated genotypes.
(E) Cdc42 reduction decreased tumor cell proliferation. Mice were pulse-labeled by BrdU for 1 hr. Note that residual villus proliferative cells remained to be detected (arrows).
(F) Numbers of crypt-like foci, BrdU+, and pHH3+ cells were reduced upon Cdc42 reduction.
(G) pHH3 staining (red) showed reduced mitotic tumor cells upon Cdc42 reduction. * indicates p<0.05 when compared to control; and # indicates p<0.05 when compared to Catnblox(ex3)/+;Vil-Cre mice. Scale bars, 5 μm.