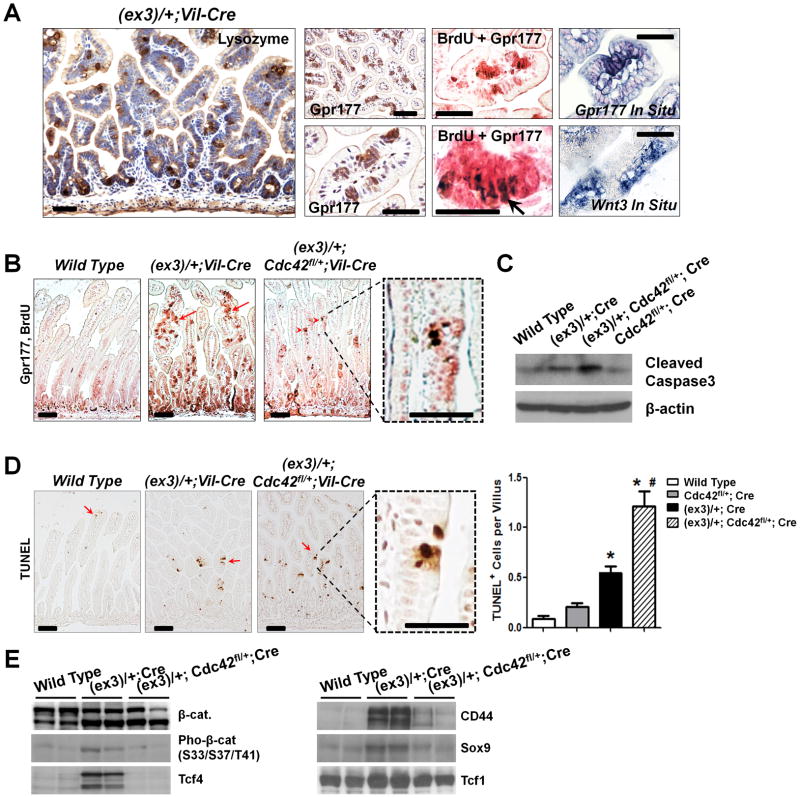
Figure 4. Fast-cycling microadenoma cells are sensitive to Cdc42 inhibition.
(A) Cells within the villus microadnoma foci in Catnblox(ex3)/+;Vil-Cre mouse intestines expressed Lysozyme, Gpr177, and Wnt3. Co-staining of Gpr177 and BrdU showed proliferative tumor cells (arrow) within the microadenoma foci.
(B) Cdc42 inhibition reduced microadnoma foci (arrows) identified by co-staining Gpr177 (pink) and BrdU (brown nuclei). Note that residual tumor cells were still detected at villi (arrowheads).
(C) Western blots for cleaved Caspase-3 showed increased apoptosis upon Cdc42 reduction.
(D) TUNEL analyses showed increased apoptotic cells (arrows) after Cdc42 reduction. Note that cell deaths were detected specifically in the ACF lesions (dotted boxes). * indicated p<0.05 comparing to wild type (Wt), and # indicated p<0.05 comparing to β-catenin mutant intestines.
(E) Loss of microadenoma cells after Cdc42 inhibition was supported by reduced levels of Tcf4, CD44 and Sox9. Note that the full length β-catenin proteins produced from the remaining wild type allele in Catnblox(ex3)/+;Vil-Cre tumor cells might be hyper-phosphorylated by GSK3β at a level higher than in control cells. Scale bars, 2 μm.