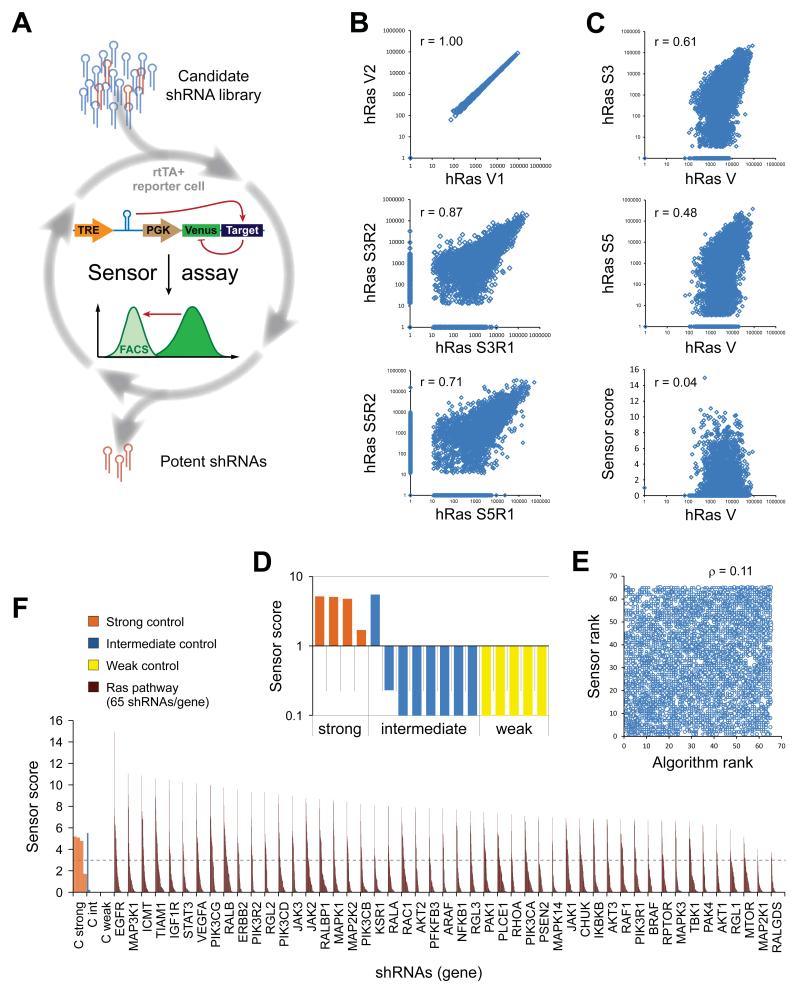
Figure 1. Functionally validated Ras pathway RNAi libraries for potent and specific gene silencing.
(A) The Sensor assay enables the generation of functionally validated shRNA libraries. The potency of candidate shRNAs was biologically probed in a pooled assay by quantifying knockdown of a Venus reporter cDNA fused to the shRNA’s cognate target site. (B-F) Human Ras set (hRas) Sensor assay results. Comparable results were obtained for the mouse Ras set (mRas, Table S1 and S2). (B) Correlations in read numbers of technical vector pool replicates (V1, V2), and biological duplicates (R1, R2) at different selection stages of the Sensor assay (S3, Sort 3; S5, Sort 5; r, Pearson correlation coefficient). (C) Correlations in read numbers between the initial vector library (mean of technical duplicates) and the endpoint populations after the indicated sorts (geometric mean of biological replicates), and the final Sensor scores. (D) Sensor scores of control shRNAs of strong (orange), intermediate (blue) or weak (yellow) potency. (E) Rank correlation between input (Algorithm rank) and output library (Sensor rank), showing that the Sensor rank is not predicted by the informatics tool (ρ, Spearman rank correlation coefficient). (F) Sensor shRNA scores for a selection of direct “Ras effector” genes (for full list see Table S2). The dotted line indicates a threshold for potent shRNAs, based on known controls. 65 shRNAs/gene; controls are represented multiple times for better visibility.