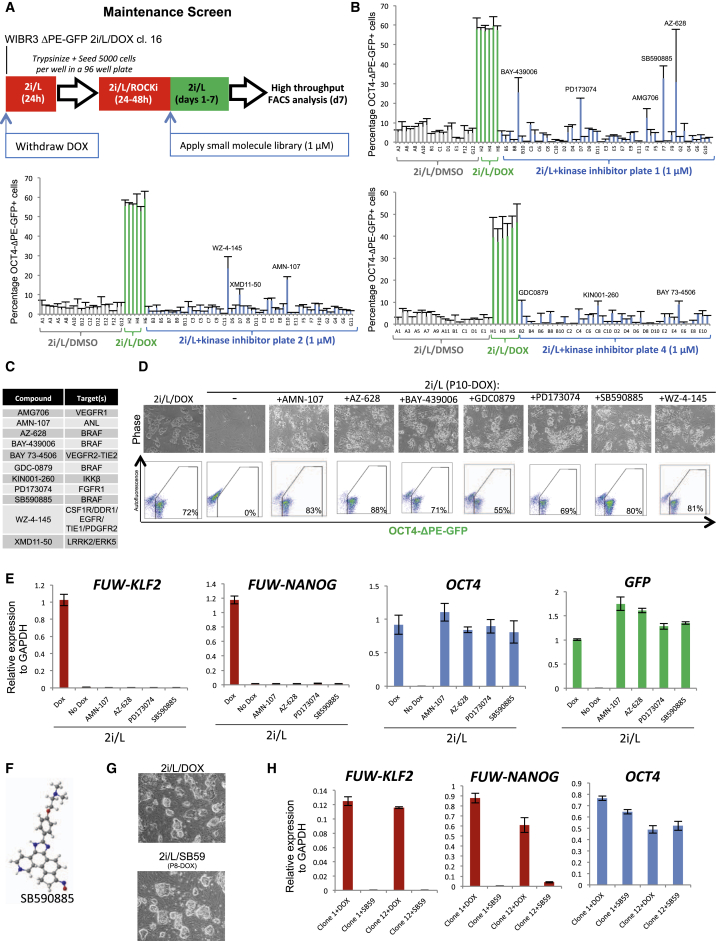
Figure 2.
Identification of Small Molecules that Maintain OCT4-ΔPE-GFP Activity after Transgene Withdrawal
(A) Strategy for screening a kinase inhibitor library to identify compounds that maintain OCT4-ΔPE-GFP reporter activity upon withdrawal of DOX-dependent KLF2 and NANOG expression.
(B) Raw data obtained from high-throughput flow cytometric analysis of the proportion of OCT4-ΔPE-GFP+ cells in 96-well plates supplemented with a kinase inhibitor library (n = 2).
(C) Hit compounds from maintenance screen using a clonal line of WIBR3 OCT4-ΔPE-GFP+ ESCs established in 2i/L/DOX.
(D) Phase images (top) and flow cytometric analysis of the proportion of OCT4-ΔPE-GFP+ cells (bottom) in a clonal line of OCT4-ΔPE-GFP+ cells derived in 2i/L/DOX and maintained for 10 passages without DOX in the presence of each candidate compound. 40× magnification.
(E) Quantitative gene expression analysis for lentiviral FUW-KLF2, lentiviral FUW-NANOG, endogenous OCT4, and GFP in a clonal line of OCT4-ΔPE-GFP+ cells maintained in 2i/L/DOX or for five passages without DOX in the presence of each candidate compound. Error bars indicate ± 1 SD of technical replicates.
(F) Chemical structure of the BRAF inhibitor SB590885.
(G) Phase images of a clonal line of WIBR3 human ESCs established in 2i/L upon DOX-mediated induction of KLF2 and NANOG (top), and the same line maintained for eight passages without DOX in 2i/L/SB590885 (1 μM) (bottom). 40× magnification.
(H) Quantitative gene expression analysis for lentiviral FUW-KLF2, lentiviral FUW-NANOG, and endogenous OCT4 in two clonal lines of WIBR3 human ESCs maintained for eight passages without DOX in 2i/L/SB590885 (1 μM). Error bars indicate ± 1 SD of technical replicates.