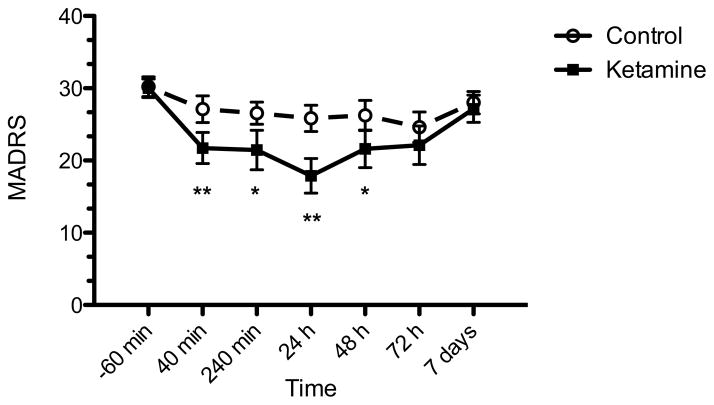
Figure 1. Change in depression severity in patients with treatment-resistant depression following intranasal ketamine or placebo.
Change in MADRS depression severity 24 hours following administration was the primary outcome measure and was significantly greater following intranasal ketamine than placebo in the modified intention-to-treat group (n=18; p<0.001). MADRS, Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; range is 0–60 with higher scores indicating greater severity of depressive symptoms. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.