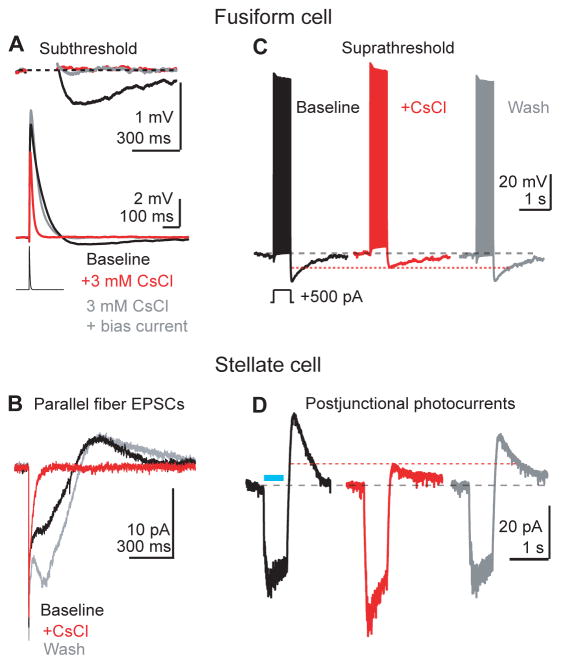
Figure 3.
Fusiform cell AHPs and stellate cell off-responses are mediated by deactivation of HCN channels.
A) An EPSC waveform (500 pA, lower trace) is injected in a fusiform cell in current clamp. CsCl (red trace) hyperpolarized the cell (see main text), and significantly shortened the half-width and reduced the peak amplitude of aEPSPs. These effects were largely reversed by returning the membrane potential to near baseline values with positive current (gray trace), showing that HCN channels control EPSP kinetics by setting the resting membrane potential near the activation range for subthreshold Na+ currents (n=7 cells. Peak amplitude baseline: 7.8±0.6 mV; CsCl 6.0±0.5 mV; CsCl + bias current: 8.8±0.6 mV. p=0.0007 and p=0.13 comparing baseline to CsCl and CsCl + Bias conditions, respectively. Repeated measures ANOVA + Dunnett's test. Half-width baseline: 47±6 ms; CsCl: 15±1 ms; CsCl + bias: 36±3 ms; p=0.002 and p=0.076 comparing baseline to CsCl and CsCl+Bias, respectively. Repeated measures ANOVA + Dunnett's test). Blocking HCN channels reduced the AHP following the depolarizing phase of the aEPSP, but adding bias current in the presence of CsCl failed to recover the AHP following the aEPSP (baseline: −0.39±0.08 mV; CsCl: −0.05 ±0.02 mV; CsCl + Bias current −0.03±0.01 mV, p= 0.014 and p=0.001 comparing baseline to CsCl and CsCl + Bias, respectively. Repeated measures ANOVA + Dunnett's test). Resting voltage of fusiform cell pre CsCl, −69 mV; in CsCl, −75 mV; in CsCl + bias current, −71 mV.
B) A stellate cell is recorded in voltage clamp. Parallel fibers are stimulated with a single shock, generating the biphasic E/I sequence shown in Figure 1B. CsCl significantly reduced the slow outward current to 1±2% of baseline (n=8. p<0.0001, one-sample t-test). Additionally CsCl hastened the timecourse of the inward component, quantified as a reduction of the EPSC inward charge transfer (n=8. 26±3% of baseline remaining, p=0.01, one sample t-test).
C) A fusiform cell is driven to spike with positive current injection. CsCl (3 mM, middle red panel) significantly reduced the amplitude of the AHP to 54±5% of baseline (n=6. p=0.0002, one sample t-test). Resting voltage of fusiform cell control, −78 mV; in CsCl: −78 mV; wash, −78 mV. Single sweeps are shown.
D) Example from a voltage-clamped stellate cell in a VGluT2-ChR2 mouse. Prejunctional fusiform cells are activated with blue light flashes through the microscope objective (blue bar), generating a biphasic postjunctional response. The outward component, which represents the fusiform cell membrane potential returning towards baseline during the AHP, was reversibly reduced by CsCl to 40±12% of baseline (n=7, p<0.0001. One sample t-test).