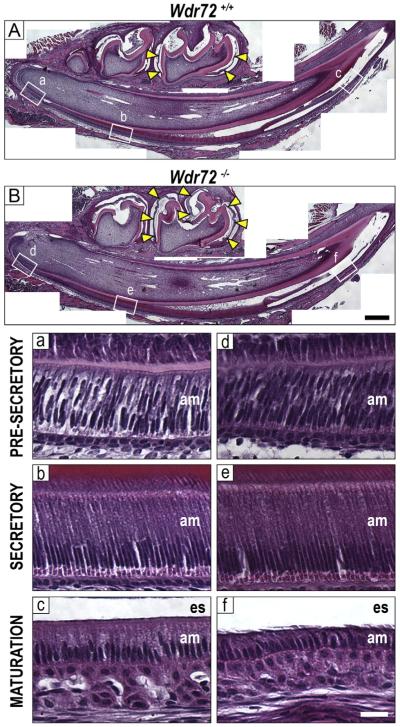
Fig. 6. Enamel matrix and ameloblasts display maturation-stage specific phenotypes in Wdr72−/− mice.
Representative sagittal sections of Wdr72+/+ (A) and Wdr72−/− (B) P10 male mandibles stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Unerupted first molars are at maturation stage, showing a lack of organic material (yellow arrows) in the enamel space of the Wdr72+/+ mice but retention in the Wdr72−/−. Lettered white boxes correspond to enlarged images below. Black scale bar, 400 μm. Bottom panels show Wdr72+/+ (a–c) and Wdr72−/− (d–f) ameloblasts at different stages of differentiation, showing the spectrum of enamel development along the continuously growing incisor. During maturation stage, Wdr72−/− ameloblasts (f) are shorter in height compared to those of Wdr72+/+ mice (c), while earlier stages appear to have morphologically normal ameloblasts. am, ameloblasts; es, enamel space. White scale bar, 20 μm. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)