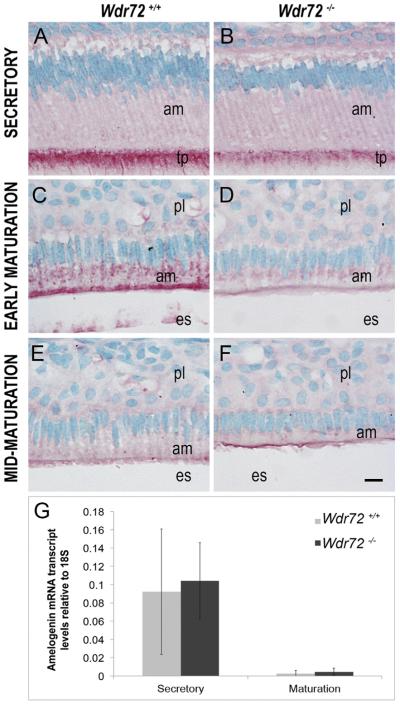
Fig. 7. Wdr72−/− ameloblast cells have decreased intracellular amelogenin proteins with no change in transcript levels.
Representative images of ameloblasts from P10 male Wdr72+/+ and Wdr72−/− mice immunostained with amelogenin antibody (red) and counterstained with methyl green. Amelogenin is immunoreactive in secretory ameloblasts at the Tomes' processes (A, B) and in early maturation-stage ameloblasts at the center and apical regions in small puncta (C, D), but was more reactive in Wdr72+/+ than Wdr72−/− mice. As enamel formation progressed to mid-maturation, intracellular amelogenin immunostaining was absent in both Wdr72+/+ (E) and Wdr72−/− (F) ameloblasts. am, ameloblast; es, enamel space; pl, papillary layer. Scale bar, 10 μm. (G) Relative amelogenin mRNA expression in microdissected enamel epithelia from 6-week-old male mice at secretory and maturation stages, showing no significant differences between Wdr72+/+ and Wdr72−/− mice at either secretory (P = 0.81) or maturation stages (P = 0.53). Gene copy numbers are relative to 18S. Error bars represent ± SD about the mean (n = 3). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)