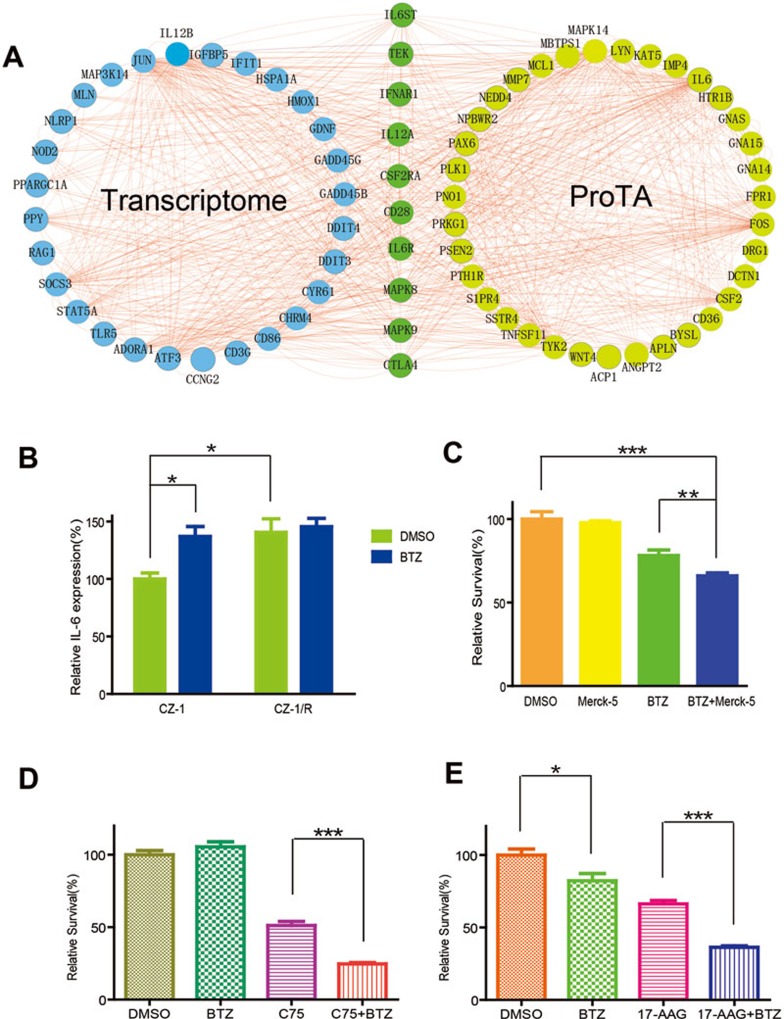
Figure 6.
Drug-resistant myeloma cells are re-sensitized to BTZ by targeting ProTA-identified hits. (A) Cross analysis of BTZ-induced changes in both human protein degradome and transcriptome. Presented here is a network summary of the results of PPI analyses performed on the top 20 hub genes extracted from the PPI-ProTA (Figure 4A) and the PPI-transcriptome data sets (Supplementary information, Figure S8). In order to profile the changes in the transcriptome of HEK293FT cells with or without BTZ treatment, total mRNAs were extracted and subjected to microarray analysis. (B) Protein levels of endogenous IL-6 in CZ-1 cells or CZ-1/R cells, with or without BTZ treatment (100 nM, 12 h). Data were represented as mean ± SEM (n = 4; *P < 0.02). (C) Cytotoxicity of BTZ (10 nM) was further enhanced by Merck-5 (2 μM, 24 h) that inhibits JAKs in IL-6 signaling pathway. Cell viability of CZ-1 was assessed with MTT assay. Data were represented as mean ± SEM (n = 6; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.0001). (D, E) BTZ-resistant CZ-1/R cells were treated with BTZ (5 nM in D, 10 nM in E) alone or in combination with C75 (D, 10 μg/ml) or 17-AAG (E, 50 μM) for 24 h. Viability of the myeloma cells in each group was assessed using MTT assay. Data were represented as mean ± SEM (n = 6; *P < 0.1; n = 6; ***P < 0.0001).