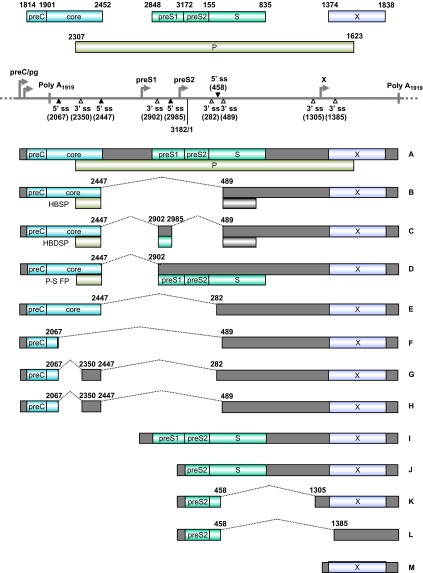
Figure 6.
Genome structure and transcription map of HBV. The full-length, circular HBV genome (GenBank: X02496.1)222 is illustrated in a linear form for better presentation of tail-to-head (3182/1) junction, four promoters (preC/pg, preS1, preS2 and X), a single poly A site at nt 1919, four alternative 5′ ss (filled triangles) and six alternative 3′ ss (open triangles). Above the linear HBV genome are viral ORFs, each with the numbered positions of the first nt of the start codon (including the in-frame start codon) and the last nt of the stop codon. Below the linear HBV genome are the RNA species (A–M) commonly derived from alternative RNA splicing, with the coding exons in colored boxes and the non-coding exons in grey boxes. The dotted lines indicate the introns and splicing directions for each RNA species, with the mapped splice site positions being numbered by nt positions in the HBV genome. HBSP, HBDSP and P-S FP are the ORFs created by alternative splicing of the preC/pg RNA. HBSP, hepatitis B splice-generated protein; HBDSP, hepatitis B doubly spliced protein; P-S FP, polymerase-surface fusion protein.