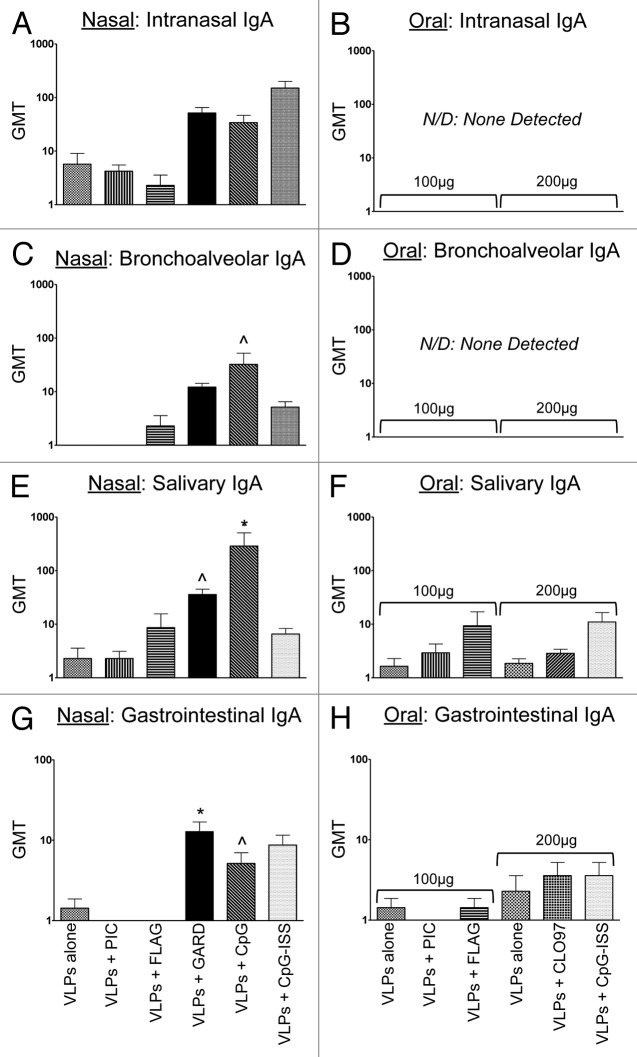
Figure 3. Evaluation of VLP-specific immunoglobulins (IgA) in distal mucosal sites (nasal, bronchoalveolar, salivary, gastrointestinal) from mice after nasal or oral vaccination. Antibody titers following nasal (A, C, E, and G) or oral (B, D, F, and H) co-delivery of VLPs with a panel of TLR agonists. Nasal vaccinations were performed using 25 μg of VLPs per dose, while oral vaccinations were performed using 100–200 μg of VLPs per dose. The panel of TLR agonists included PIC (TLR3), FLAG (TLR5), GARD (TLR7), CpG (TLR9), CpG-ISS (TLR9, alternate CpG motif), and CL097 (TLR7/8). Geometric mean titers (GMT) of all serum samples were determined by ELISA. Immunoglobulins analyzed in mucosal samples included intranasal IgA (A and B), bronchoalveolar IgA (C and D), salivary IgA (E and F), and gastrointestinal IgA (G and H). Nonparametric t tests were performed between each mucosal sample and samples collected from mock-immunized mice. Statistical significance: ^P < 0.05, *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.