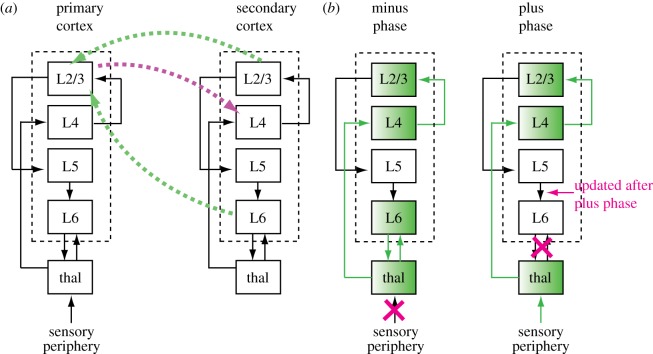
Figure 1.
Neocortical anatomy supporting LeabraTI. (a) Cortical areas are composed of columns of neurons with canonical circuitry within and between areas. Within a column, information follows the path Layer 4 → Layer 2/3 → Layer 5 → Layer 6. Layer 2/3 sends feedforward projections to the next area and is the primary site of feedback, and thus can be seen as doing bidirectional information processing. (b) Layer 5 neurons integrate contextual information from Layer 2/3 → Layer 5 synapses, and gate this context signal into Layer 6 neurons. These Layer 6 neurons sustain the context via recurrent projections through the thalamus, which also recirculate the context through the local column to support generation of the next prediction during the minus phase. Veridical information from the sensory periphery drives the column in the plus phase. Layer 6 context is not used during the plus phase but is updated through the Layer 2/3 → Layer 5 → Layer 6 intra-columnar circuit at the end of processing (every 100 ms). thal, thalamus. (Online version in colour.)