Figure 8.
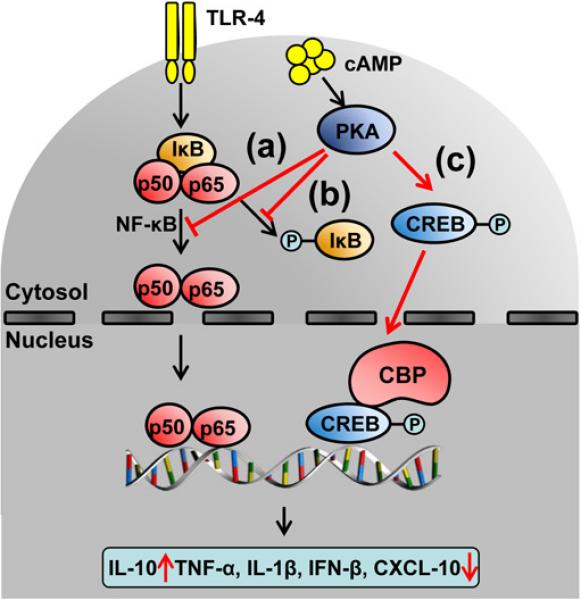
The molecular mechanisms of cAMP-PKA mediated inhibition of TLR-4 – NF-κB axis. The activation of cAMP-PKA: (a) directly prevents NF-κB translocation; (b) stabilizes IκB inhibitor; (c) induces phosphorylation of the CREB, which owing to its high affinity for the co-activator CREB-binding protein (CBP), suppresses the association of CBP with p65. Such transcriptional machinery is perfectly assembled to selectively promote IL-10, but not pro-inflammatory TNF-α, IL-1β, IFN-β and CXCL-10.
