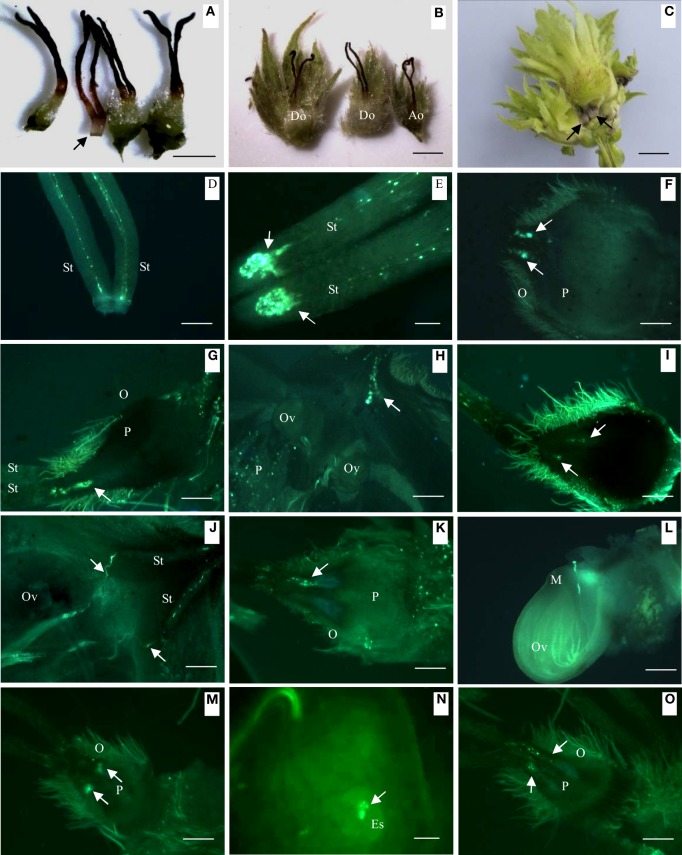
Figure 1.
Differences in external morphology and pollen tube growth in developing and abortive ovaries during the progamic phase. (A) External morphology of abortive ovary (indicated by arrow) and developing ovary, 30 days after blooming. (B) Normally developing ovary (left and center) and abortive ovary (right), 40 days after blooming. (C) Normally developing fruit and abortive fruit in a fruit cluster, 65 days after pollination. Arrows indicate abortive ovaries. (D) Young pollen tubes in the style, 5 days after blooming. (E) Pollen tubes curled and arrested at the style base, showed by arrows, 20 days after blooming. (F) Pollen tubes growing into developing ovary, arrows showed pollen tubes, 40 days after blooming. (G) Pollen tubes (showed by arrow) growing into abortive ovary, 40 days after pollination. (H) Pollen tubes (showed by arrow) growing toward ovule, 45 days after pollination. (I) Pollen tubes arrested in abortive ovary (showed by arrow), 45 days after pollination. (J) Pollen tubes in style (showed by arrow) changed direction and grew toward ovule, 50 days after pollination. (K) Pollen tubes arrested in abortive ovary, 50 days after pollination. (L) Pollen tubes starting to penetrate ovule of developing ovary, 55 days after pollination. (M) Abortive ovary with Curled and arrested pollen tubes, 55 days after pollination. (N) Pollen tubes in developing ovary release two sperm cells in embryo sac, 60 days after blooming. (O) Abortive ovary with curled and arrested pollen tubes, 60 days after blooming. Key: Ao, abortive ovary; Do, developing ovary; Es, embryo sacs; M, micropyle; O, ovary; Ov, ovule; P, parenchyma; St, style; Scale bars: A,B = 1 mm; C = 400 μm; D = 300 μm; E = 100 μm; F–O = 300 μm.