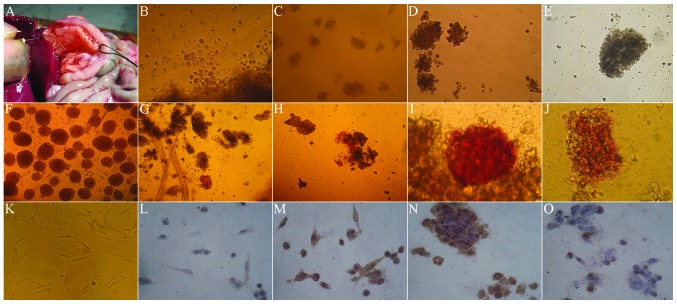
Figure 2.
Morphology, dithizone and PDX-1 staining of hUC-MSCs in Wharton’s Jelly co-cultured with rat’s islet cells (magnification, ×100). (A) Extraction of rat islet cells. (B) In the first few days of co-culture with the rat islet cells, hUC-MSCs rapidly became spherical. (C) In the 7 days of co-culture, the spherical cells gradually accumulated and became a large cell mass. (D) In the 10 days of co-culture, the spherical cells gradually accumulated and became a large cell mass. (E) After 14 days, the cells aggregated and became a larger cell mass. (F) The cytoplasm was brownish-red under dithizone staining, indicating strong positive. (G) At day 3 of co-culture with the rat islet cells, the dithizone staining of hUC-MSCs was negative. (H) At day 7 of co-culture with the rat islet cells, the dithizone staining presented strong brownish red. (I) At day 10 of co-culture with the rat islet cells, the dithizone staining presented strong brownish red. (J) At day 14 of co-culture with the rat islet cells, the stained cells were comparatively rare in dithizone staining. (K) Prior to culture, the hUC-MSCs were long fiber-shaped or fusiform-shaped. (L) At day 3 of co-culture with the rat islet cells, the PDX-1 staining of hUC-MSCs was negative. (M) At day 7 of co-culture with the rat islet cells, the PDX-1 staining presented strong brownish. (N) At day 10 of co-culture with the rat islet cells, the PDX-1 staining presented strong brownish. (O) At day 14 of co-culture with the rat islet cells, the stained cells were comparatively rare in PDX-1 staining. PDX-1, pancreatic and duodenal homeobox-1; hUC-MSCs, humal umbilical cord mesenchymal cells.