Figure 4.
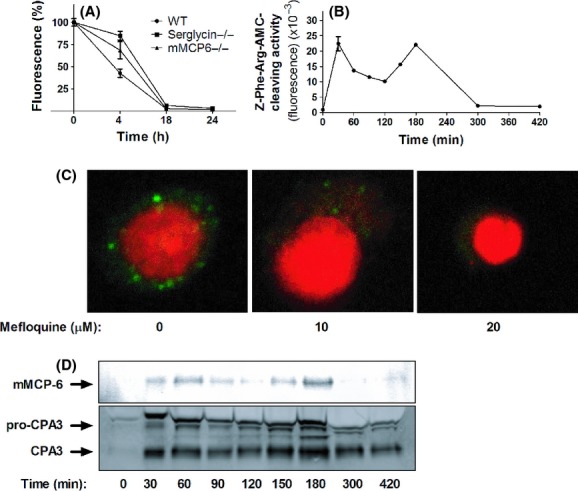
Mefloquine causes secretory granule permeabilization in mast cells. (A) Bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) (WT, serglycin−/− or mMCP-6−/−; 0.5 × 106 cells) were cultured in the absence or presence of 10 μmol/L mefloquine for the time periods indicated, followed by staining with AO. Results are expressed as % fluorescence in comparison with nontreated control cells (mean ± SEM, n = 3). (B) Z-Phe-Arg-AMC-cleaving activity present in the cytosol after treatment of BMMCs (106 cells) with 10 μmol/L mefloquine. After addition of mefloquine, cytosolic extracts were prepared at the time points indicated and were analyzed for Z-Phe-Arg-AMC-cleaving activity. (C) BMMCs (106 cells) were treated with the indicated concentrations of mefloquine. After 3 h of incubation, cells were stained with LysoTracker (green) to visualize acidic compartments and nuclei were visualized by DAPI staining (Red). (C) BMMCs (106 cells) were treated with 10 μmol/L mefloquine. At the time points indicated, cytosolic extracts were prepared and subjected to western blot analysis for presence of granule proteases (mMCP-6 and CPA3).
