Figure 3.
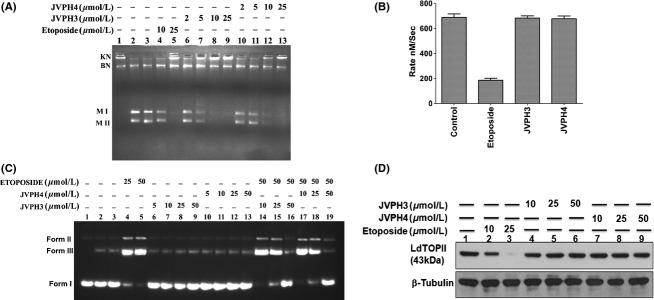
Inhibitory activity of isobenzofuranone derivatives on LdTOPII. Purified LdTOPII was incubated with 200 ng kDNA in presence of different concentrations of JVPH3 and JVPH4. Lane 1, kDNA only; lane 2, kDNA treated with LdTOPII; lane 3, same as lane 2 but in presence of DMSO. KN and BN indicate kDNA network and broken network, respectively. M II and M I indicate the released minicircles super coiled and nicked form (A). ATPase activity of LdTOPII was measured by the pyruvate kinase/lactate dehydrogenase assay. Rate of LdTOPII-mediated ATP hydrolysis in presence of (50 μmol/L) etoposide and 50 μmol/L of JVPH3/JVPH4 were measured (B). The results are shown as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Inhibition of etoposide-induced cleavage complex formation by isobenzofuranone derivatives was analyzed by cleavage reaction and agarose gel electrophoresis. Lane 1, negatively supercoiled pRYG DNA; lane 2, pRYG DNA with LdTOPII alone; lane 3 same as lane 2 but in presence of proteinase k treatment (C). In vivo LdTOPII-mediated cleavage complex stabilization by isobenzofuranone derivates was analyzed by immunoband depletion assay. Equal amounts of protein from different treatments were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with antibody raised against ATPase domain of LdTOPII. β-tubulin served as loading control (D).
