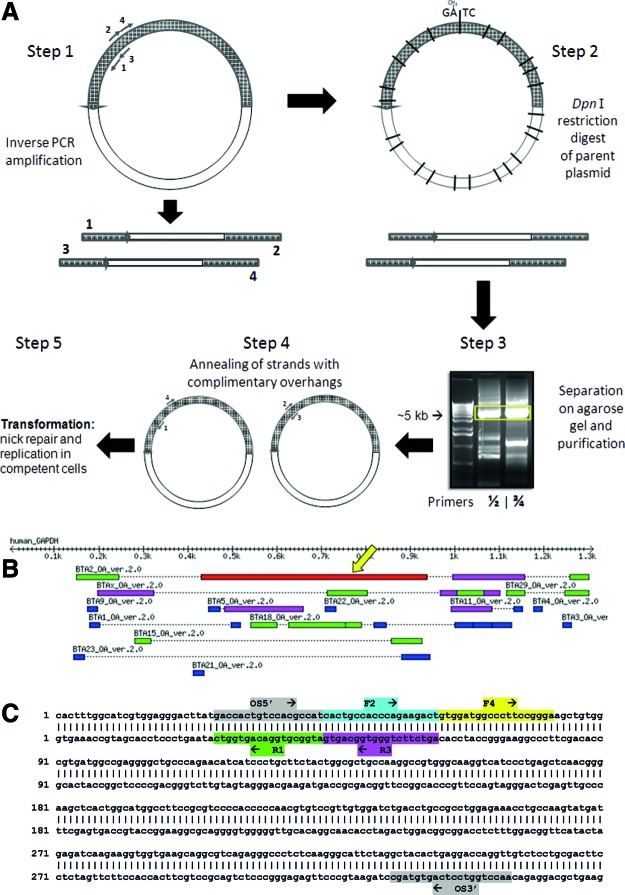
FIG. 2.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based method for isolation of specific clones from a complimentary DNA library pool. (A) Two PCRs were performed using two sets of inverse and abutting primers. The parent library was digested with DpnI restriction enzyme after which the PCR products are separated on an agarose gel and bands of equal sizes (∼5 kb) cut out and purified. The purified PCR products were combined in a single tube and denatured and annealed. Only strands with complementary overhangs, that is, 1+4 or 2+3, formed nicked circles, which when transformed into competent cells are repaired and replicated as circular plasmids. (B) The coding sequence of human glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) mRNA sequence was BLAST searched against the sheep genomic database to find an appropriate region in which to place the MACH primers. (C) The arrangement of the forward and reverse MACH primers is seen here. Two separate PCRs are set up with the inverse and abutting primer pairs R1/F2 and R3/F4. The outside (OS) primers are used to determine the abundance of the clone of interest. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tec