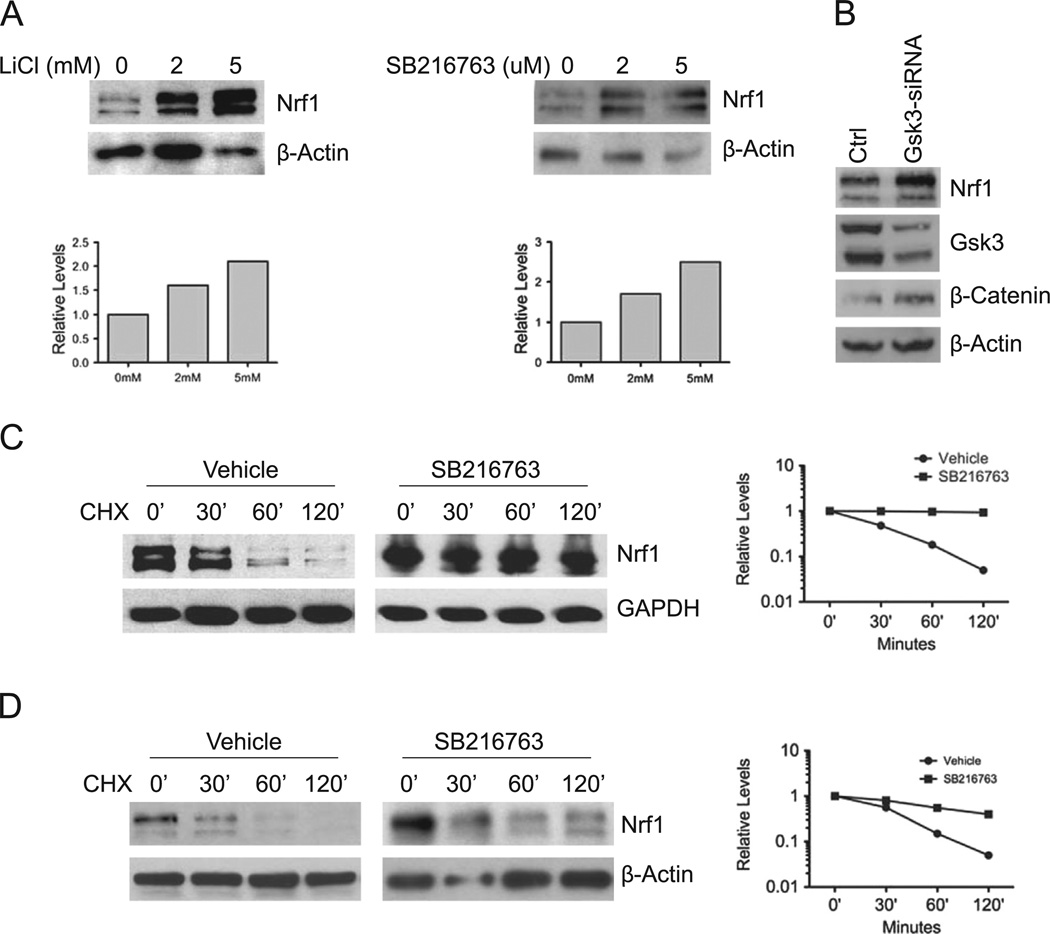
Fig. 1. GSK3 modulates Nrf1 expression.
(A) HEK293 cells were treated with LiC1 or SB216763 at the indicated concentrations for 16 h, and whole cell extracts were immunoblotted with anti-Nrf1 antibody. In accord with previous findings, two major immunoreactive bands representing glycosylated and non-glycosylated forms of Nrf1 were detected [21]. Beta-actin levels were used as loading control. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with a mixture of the two siRNAs against GSK3. After 48 h, lysates were Western blotted for Nrf1 levels. Western blotting was also done to verify the level of GSK3 knockdown and concomitant increase in β-Catenin protein as control. Beta-actin levels were used as loading control. (C) HEK293 cells were treated with 10 µM SB216763 for 16 h, followed with 50 µg/ml cycloheximide, and cells were harvested at the indicated time points. Whole cell extracts were immunoblotted with anti-Nrf1 antibody. Beta-actin levels were used as loading control. (D) Mouse embryonic fibroblasts were treated with SB216763 for 16 h, followed by 50 µg/ml cycloheximide, and cells were harvested at the indicated time points. Whole cell extracts were prepared and immunoblotted against Nrf1. Beta-actin levels were used as loading control. Graphs show quantitation of protein levels.