Figure 11. Endogenous cytokeratin 5 (K5) is detected in the labyrinthine layer and yolk sac of control E12.5 placentas.
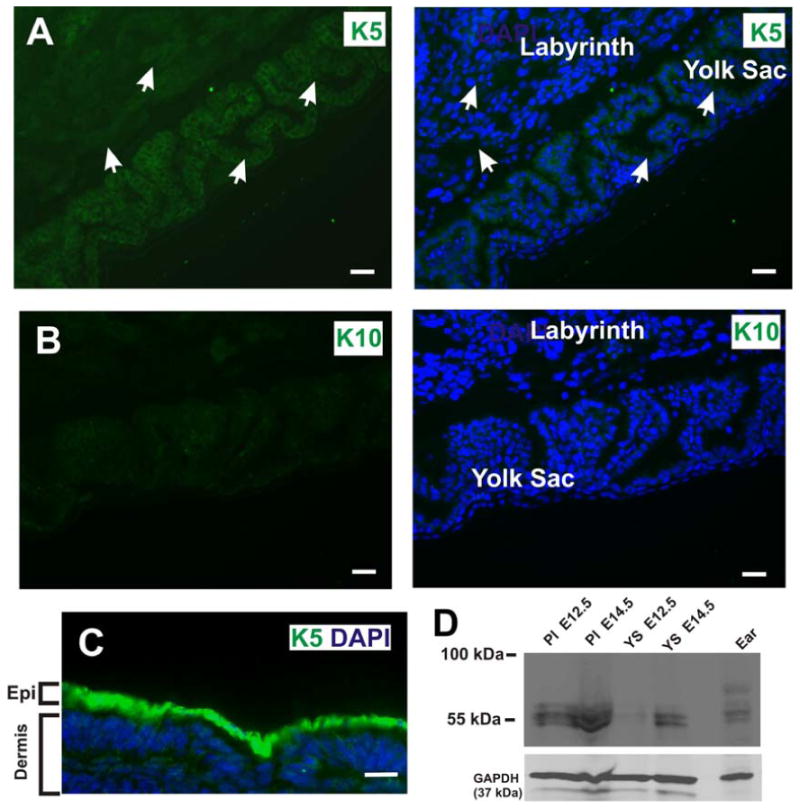
(A) The labyrinthine layer and yolk sac epithelia are derived from the trophectoderm and primitive endoderm, respectively. Wide field conventional immunofluorescence microscopy of frozen tissue sections of the E12.5 placenta revealed that the labyrinthine layer and yolk sac express endogenous K5, a basal cell marker. White arrows denote K5 expression in the labyrinthine layer and yolk sac. Blue is nuclear DAPI stain. (B) In contrast, no immunofluorescent signal is detected in the labyrinthine layer or yolk sac with an antibody against cytokeratin 10, a suprabasal marker. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of frozen cross section of E12.5 embryonic epidermis with a anti-cytokeratin 5 antibody (green). Scale bars, 25 μm. (D) Western blot of placenta (Pl) and yolk sac (YS) lysates at E12.5 and E14.5. Ear tissue lysate was used as a positive control for K5 expression. The lower portion of the same filter was probed for GAPDH as a loading control
