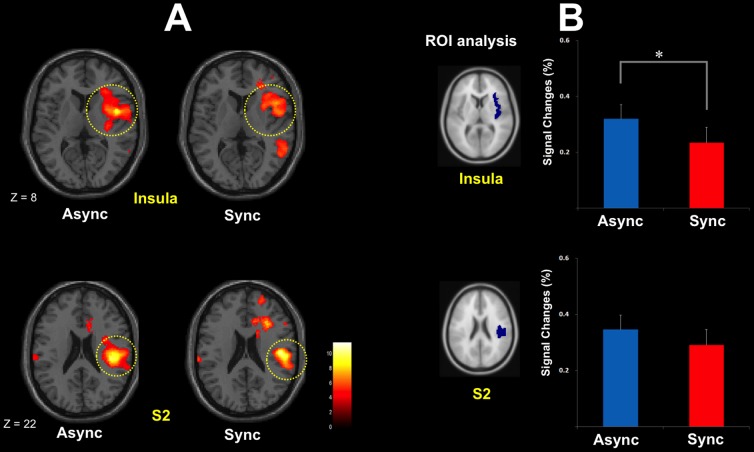
Figure 3. Brain activations in response to acupuncture stimulation.
A: Brain activations in response to acupuncture stimulations were observed in the contralateral secondary somatosensory cortex (SII) and insula under both the asynchronous (right SII: 44, −26, 26; t = 11.52; Z = 5.9; right insula: 44, 2, 8; t = 9.78; Z = 5.5) and synchronous (right SII: 50, −20, 20; t = 9.33; Z = 5.39; right insula: 56, 20, 0; t = 8.9; Z = 5.27) conditions. All two peaks were p<0.05, corrected, and all coordinates are in MNI space. B: To plot the regions of brain activation involved in acupuncture stimulation, the averaged percent signal change in anatomical regions of interests (ROIs), including the right insula and SII, were extracted. When the acupuncture stimulation occurred, BOLD responses in the right insula (0.32±0.04 vs. 0.23±0.05%, t = 2.517, P<0.05; A) but not the SII (0.34±0.05 vs. 0.29±0.05%, t = 1.413, P>0.177; B) differed significantly under the asynchronous and synchronous sessions.