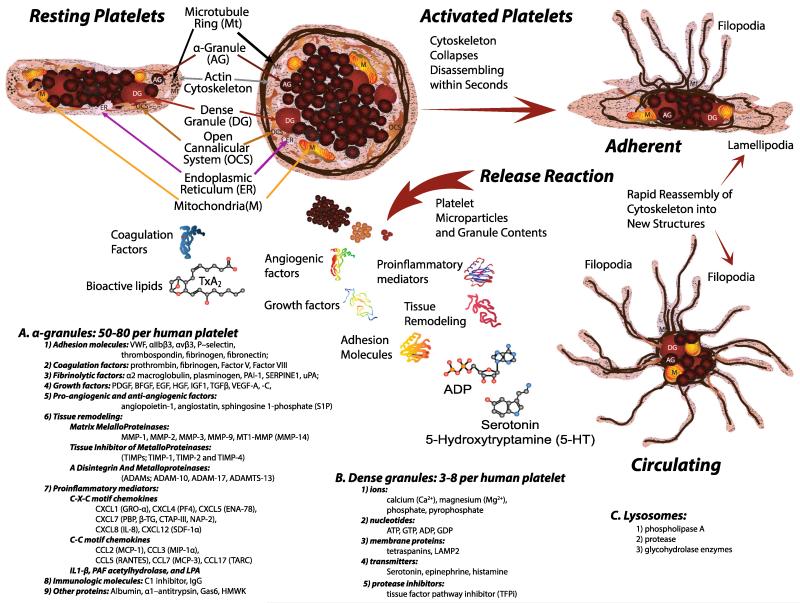
Fig. 2.
Resting platelets maintain their discoid shape using a structural ring of microtubules (Mt) and actin cytoskeleton. The plasma membrane is connected to an internal membrane reservoir called the open canalicular system (OCS). Platelets also contain organelles including endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and mitochondria (M). Resting platelets carry stores of bioactive contents in a granules (a), dense granules (b), and lysosomes (c) that are released following activation. Once activated, the platelet cytoskeleton collapses followed by extensive shape change depending upon the trigger stimulus. Lamellipodia are formed when in contact with flat surfaces such as extracellular matrix, and facilitate platelet migration. Filopodia that promote contact with other platelets or cells are formed by adherent and circulating platelets in suspension