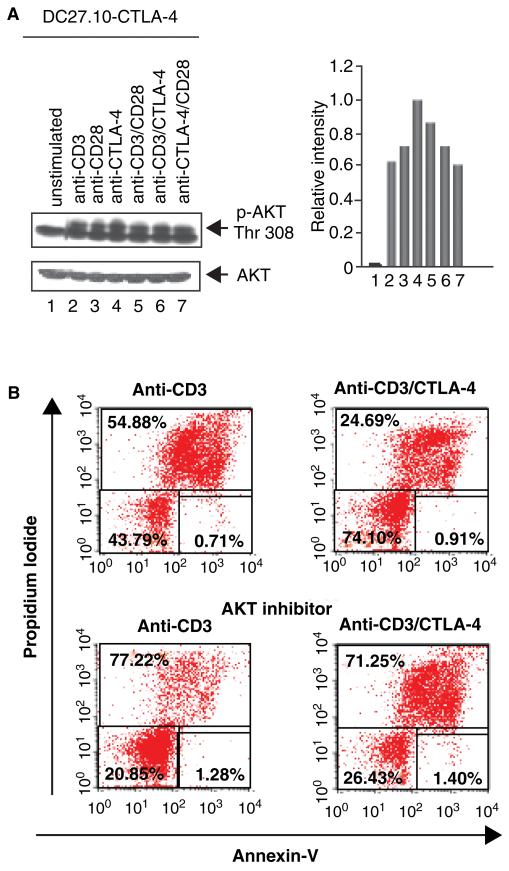
Fig. 4. CTLA-4 coligation can rescue T cells from AICD under conditions of anergy induction.
(A) CTLA-4 coligation induces AKT–Thr–308 phosphorylation. DC27.10–CTLA-4 cells were left untreated (lane 1) or stimulated for 30 min with anti-CD3 (lane 2), anti-CD28 (lane 3), anti-CTLA-4 (lane 4), anti-CD3/CD28 (lane 5), anti-CD3/CTLA-4 (lane 6), and anti-CD28/CTLA-4 (lane 7) antibodies. The DC27.10 cell is a mouse hybridoma that has been stably transfected with CTLA-4 (i.e. DC27.10–CTLA-4). Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-phospho-PKB/AKT (Thr-308) antibody (lanes 1–7). Lower panel: equal amounts of cell lysates were detected by anti-PKB/AKT blotting (lanes 1–7). Histogram depiction of phosphorylated PKB/AKT as detected by densitometric reading. Similar observations were made in peripheral T cells (86). (B) CTLA-4 coligation can rescue T cells from AICD in an AKT/PKB-dependent manner. Pre-activated PBLs were stimulated with anti-CD3 (left panel) and anti-CD3/CTLA-4 (right panel) in the absence (upper panel) or presence of AKT inhibitor (AKT inhibitor II) (lower panel). CTLA-4 coligation reversed cell death induced by anti-CD3 (i.e. 54% to 24% cell death), an event reversed by the inhibition of AKT/PKB (i.e. 77% and 71% cell death) and PI3K (data not shown). Cell viability was assessed by staining with Annexin V-Cy5 and propidium iodide and analyzed using FACS. CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4; AICD, antigen-induced cell death; PKB, protein kinase B; PBL, peripheral blood lymphocyte; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.