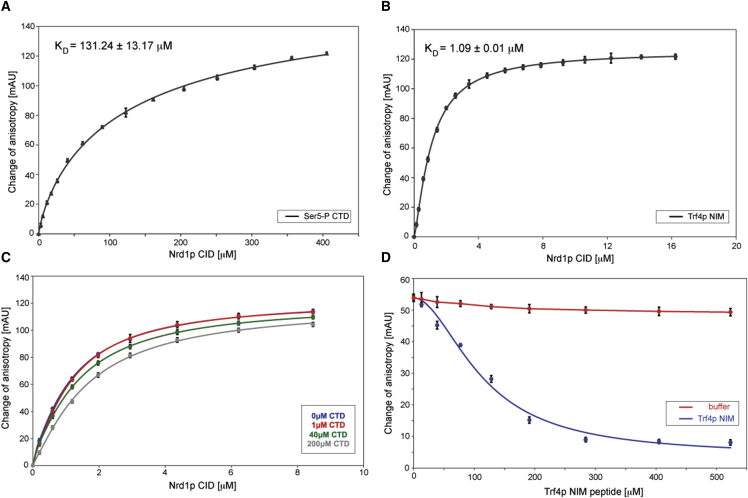
Figure 3.
Fluorescence Anisotropy Analyses of Nrd1p CID Binding to Trf4 NIM and the CTD
(A and B) Equilibrium binding of Nrd1p CID with Ser5P CTD (A) and Trf4p NIM (B) fluorescently labeled peptides monitored by fluorescence anisotropy (FA). Binding isotherms and dissociation constant (KD) are shown.
(C) FA competition assays between Ser5P CTD and Trf4p NIM for binding to Nrd1p CID. Samples containing 10 nM FAM-labeled Trf4p NIM peptide and 0 μM (blue), 1 μM (red), 40 μM (green), or 200 μM (gray) of unlabeled Ser5P CTD were titrated with Nrd1p CID. Displacement of the binding isotherm with increasing concentration of Ser5P CTD indicates competition for binding to Nrd1p CID.
(D) FA competition assays between pSer5 CTD and Trf4p NIM for binding to Nrd1p CID with a different experimental setup compared to (C). Preformed complex of 10 nM FAM-labeled Ser5P CTD and Nrd1p CID (120 μM final protein concentration) was titrated with different amounts of Trf4p NIM peptide (blue) or buffer (red) as a control. The decrease of fluorescence anisotropy reflects the disassembly of the Ser5P CTD-Nrd1p CID complex.