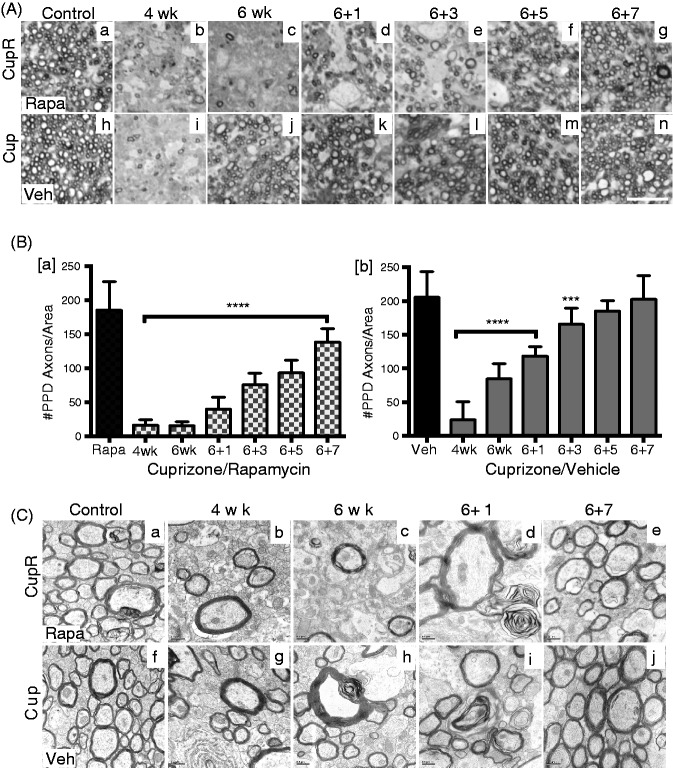
Figure 2.
Slower remyelination occurred after treatment with cuprizone plus rapamycin compared with cuprizone alone. (A) Semithin sections (2 µm) were stained with PPD to visualize myelinated axons over a large area of the corpus callosum. Representative areas show control levels of PPD-stained axons in rapamycin-treated (Rapa, a) or vehicle-treated (Veh, h) animals on regular diet compared with the demyelination at 4 and 6 weeks with cuprizone plus rapamycin treatment (b, c) and cuprizone plus vehicle (i, j). The extent of remyelination at 1, 3, 5, and 7 weeks of recovery appeared to be less with CupR (d to g) than with Cup (k to n). Images were captured using a Zeiss 100 × oil Plan-Apochromat objective (NA 1.3). Scale bar = 10 µm. (B[a,b]) Demyelination and remyelination were quantified in PPD-stained sections by manually counting the number of myelinated axons in each 400 µm2 area (see the “Materials and Methods” section). Values are the mean ± SD analyzed by one-way ANOVA. ***p < .001, ****p < .0001, with Bonferonni’s correction for multiple comparisons. For each time point, n = 2 animals per treatment. (C) EM analysis of ultrathin sections was used to visualize the ultrastructure of myelin in the two treatments groups. Representative rapamycin-only treated tissue (a) compared with cuprizone plus rapamycin (top panel) at 4 or 6 weeks (b, c), and recovery times of 1 week (d) and 7 weeks (e). Vehicle-only tissue (f) compared with cuprizone-treated tissue (bottom panel) at 4 weeks (g) or 6 weeks (h) of treatment, and recovery times of 1 week (i) and 7 weeks (j). Scale bar = 0.5 µm. Cup = cuprizone alone; CupR = cuprizone plus rapamycin; Rapa = rapamycin alone; Veh = vehicle alone; PPD = para-phenylenediamine.