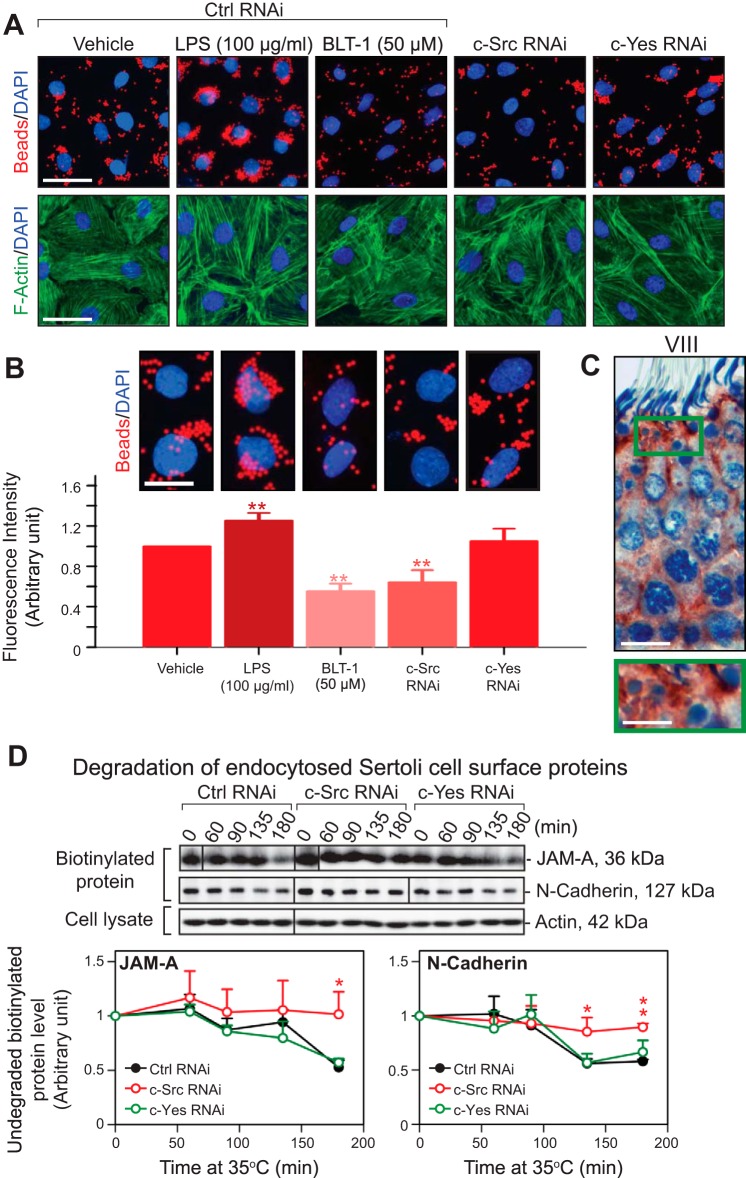
Fig. 4.
c-Src is involved in Sertoli cell phagocytosis and endocytic vesicle-mediated protein degradation at the Sertoli cell BTB in vitro. A: Sertoli cells after being transfected with either c-Src or c-Yes siRNA duplexes vs. control duplexes were assessed on their phagocytic activity using FluoSpheres fluorescent microspheres. Phagocytosis of the microspheres was induced following treatment with LPS, a phagocytosis inducer, but blocked by block lipid transport-1 (BLT-1), a phagocytosis inhibitor. Knockdown of c-Yes had no effects on Sertoli cell phagocytosis activity, but the knockdown of c-Src impeded Sertoli cell phagocytosis. Both BLT-1 treatment and c-Src and c-Yes RNAi were also found to induce actin microfilament truncation but not LPS treatment. Scale bar, 45 μm (which applies to other micrographs). B: each bar is the mean ± SD of n = 6 experiments; enlarged images highlight representative findings of changes in phagocytic activity of Sertoli cells on the fluorescent microspheres. C: immunohistochemical localization of c-Src in the seminiferous epithelium of a stage VIII tubule, illustrating the intense localization of immunoreactive c-Src in residual bodies. Boxed green area is magnified and shown below the micrograph. Scale bar, 25 μm (12.5 μm in magnified image). D: kinetics of degradation was estimated in a biochemical assay in which the disappearance of total cell surface and intracellular biotinylated/endocytosed JAM-A or N-cadherin was assessed following the knockdown of c-Src or c-Yes vs. nontargeting control in Sertoli cell BTB in vitro. β-Actin served as protein loading control. Each bar in the line graph is the mean ± SD of n = 4 experiments. The knockdown of c-Src, but not c-Yes, was found to impede the degradation of endocytosed cell surface JAM-A and N-cadherin. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.