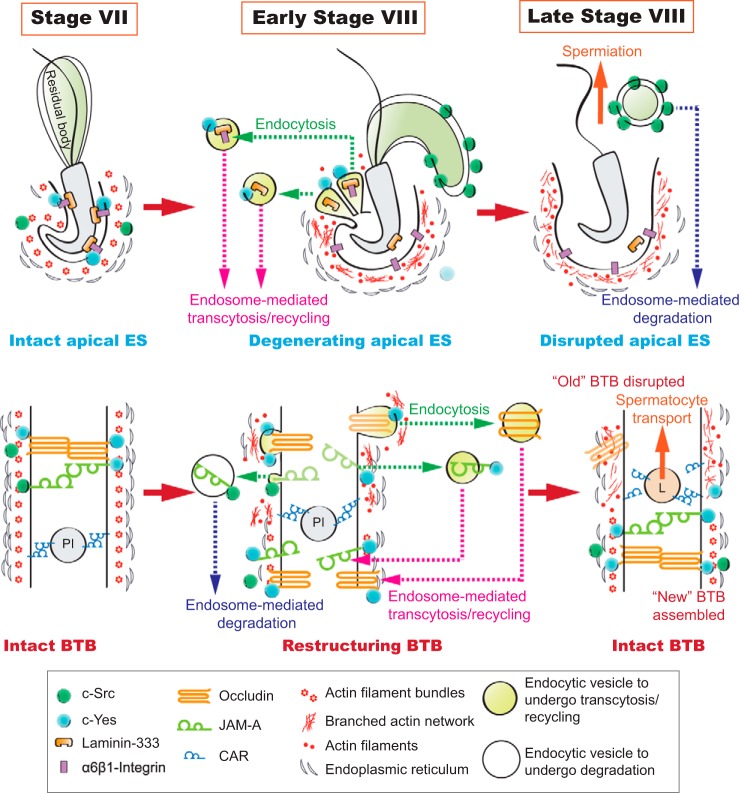
Fig. 5.
A hypothetical model illustrating the differential roles of c-Yes and c-Src in endocytic vesicle-mediated trafficking that maintain BTB homeostasis during the epithelial cycle. This hypothetic model regarding the differential roles of c-Yes and c-Src in endocytic vesicle-mediated protein trafficking was prepared on the basis of findings reported herein. As shown at top during the degeneration of apical ectoplasmic specialization (ES) to facilitate the release of step 19 spermatids from the seminiferous epithelium once they are transformed to spermatozoa, c-Src assists the formation and/or degradation of residual body derived from spermiogenesis. On the other hand, c-Yes assists endocytic vesicle-mediated protein endocytosis, transcytosis, and/or recycling so that proteins at the “old” apical ES (top) or old BTB (bottom) can be recycled to assemble “new” apical ES or new BTB in stage VIII of the cycle.