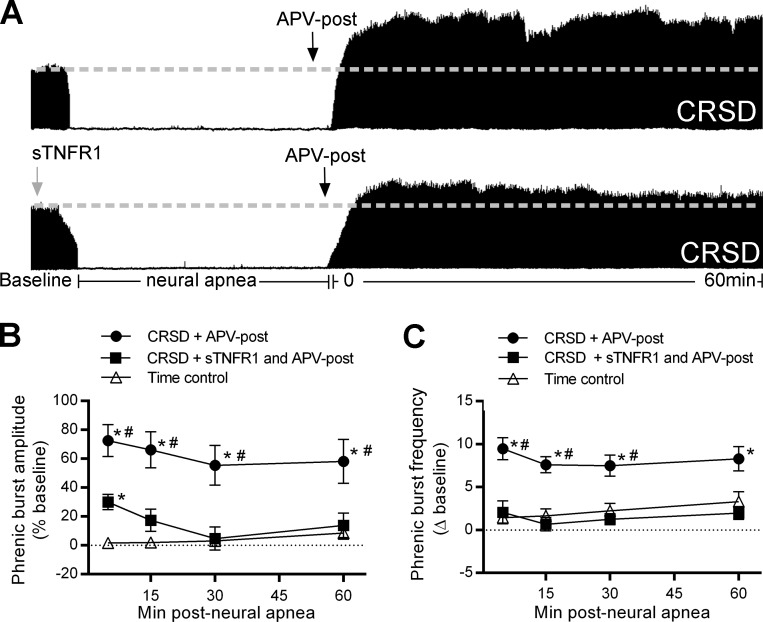
Fig. 3.
Long-lasting iPMF in CRSD rats receiving APV requires spinal tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). A: representative compressed phrenic neurograms during baseline, 30 min of neural apnea, and for 60 min after the resumption of phrenic neural activity in CRSD rats receiving intrathecal APV shortly prior to the resumption of respiratory neural activity (APV-post) or TNF-α signaling inhibitor, soluble TNF-α receptor 1 (sTNFR1) and APV-post. Black arrows denote intrathecal delivery of APV-post; gray arrow indicates intrathecal delivery of sTNFR1. B: average phrenic burst amplitude (% baseline) for 60 min post neural apnea or an equivalent duration in time controls (triangles) in rats receiving APV-post (circles) or pretreatment of sTNFR1 and APV-post (squares). CRSD rats receiving APV-post expressed a significant increase in phrenic burst amplitude relative to time controls at all time points post neural apnea, indicating long-lasting iPMF. By contrast, CRSD rats receiving sTNFR1 and APV-post expressed a small but significant increase in phrenic burst amplitude compared with time controls at 5 min post neural apnea; however, phrenic burst amplitude was not significantly increased from time controls at subsequent time points. Furthermore, phrenic burst amplitude in CRSD rats receiving sTNFR1 and APV-post was significantly lower than in CRSD rats receiving APV-post at all time points post neural apnea, indicating that long-lasting iPMF in CRSD rats with NMDAR inhibition requires spinal TNF-α. C: average phrenic burst frequency (Δ baseline) for 60 min post neural apnea or an equivalent duration in time controls (triangles) in rats receiving APV-post (circles) or sTNFR1 and APV-post (squares). CRSD rats receiving intrathecal APV-post expressed a significant increase in phrenic burst frequency from time controls at all time points. By contrast, phrenic burst frequency in CRSD rats receiving sTNFR1 and APV-post was not significantly increased from time controls at any time point following neural apnea. Values are means ± SE. *Significantly different than time controls; #significantly different than sTNFR1 and APV-post; P < 0.05.