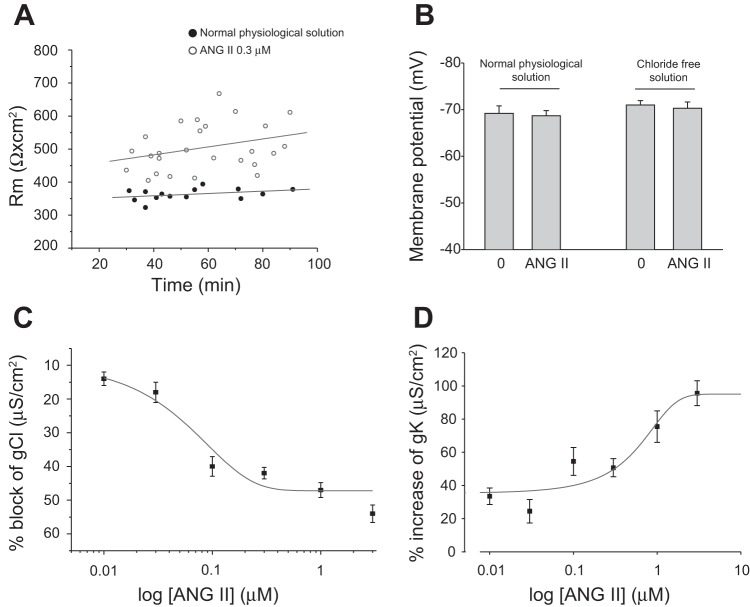
Fig. 1.
Effect of in vitro application of ANG II on membrane resistance, resting membrane potential, and resting conductance to chloride and potassium ions of extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscle fibers of wild-type (WT) mice. A: membrane resistance (Rm) plotted as a function of time (in min). The chart shown the Rm values in the absence (●) and in the presence of ANG II (0.3 μM; ○). B: resting membrane potential in fiber sampled for the Rm values in the absence and in the presence of ANG II (0.3 μM) both in normal physiological solution and in chloride-free solution. Values are means ± SE from 59–81 fibers from 6–15 preparations. C and D: percent block of chloride conductance (gCl) and percent increase of potassium conductance (gK), respectively, as a function of increasing concentrations of ANG II. Each point is the means ± SE from 12–56 fibers from 3–4 muscle preparations. All values are statistically different with respect to the value in the absence of ANG II (0.001<P < 0.01 by Student's t-test).