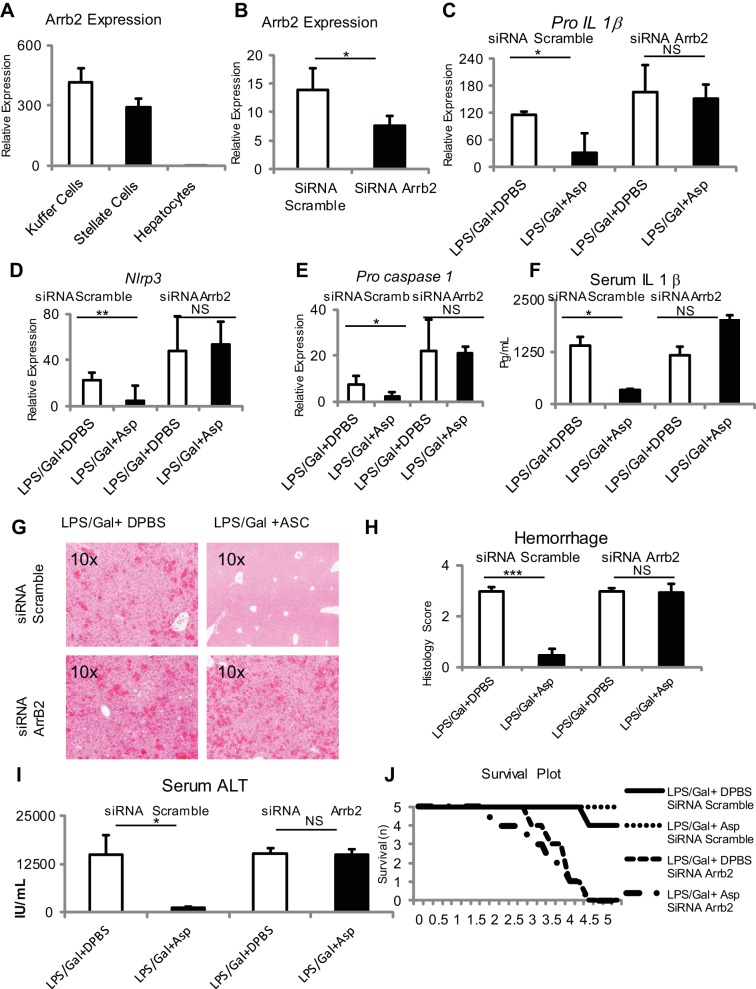
Fig. 5.
β-Arrestin is required for dampening proinflammatory responses in vivo, and aspartate supplementation can further dampen proinflammatory responses in vivo. A: β-Arrestin is strongly expressed in Kupffer cells and stellate cells relative to hepatocytes. B: Selective knockdown of β-arrestin is achieved in whole liver using Invivofectamine and β-arrestin targeting siRNA as determined by β-arrestin transcript. In vivo knockdown of β-arrestin results in significant loss of aspartic acid-mediated suppression of LPS d-galactosamine-induced Pro-Il1β (C), Nlrp3 (D), and Pro-caspase-1 (E) expression in the liver, serum IL-1β release in the serum (F), liver hemorrhage (G and H), serum ALT values (I), and progression of injury to mortality (J) in mice treated with LPS and d-galactosamine at 5 h posttreatment. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.