Figure 5.
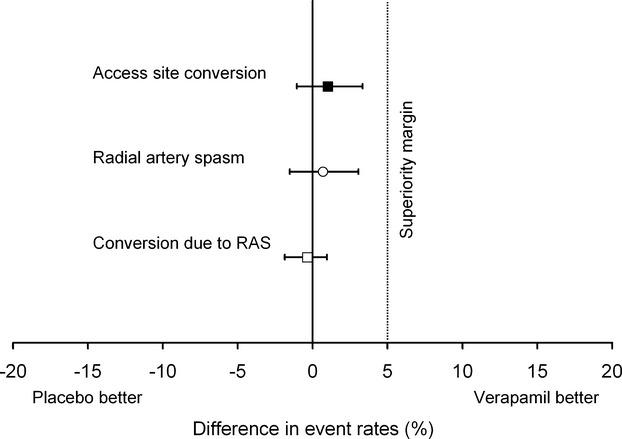
Treatment effect of verapamil for access site conversion, radial artery spasm, and access site conversion due to radial artery spasm. All 2‐sided 95% CIs for the differences in event rates overlap zero and do not cross the prespecified superiority margin of 5%, suggesting that the policy of prophylactic verapamil application may not be superior to the strategy of ad hoc administration (difference in access site conversion rates: 1.0%, 95% CI −1.1% to 3.3%; difference in rate of radial artery spasm [RAS]: 0.7%, 95% CI −1.5% to 3.1%; difference in occurrence of access site crossover due to RAS: −0.3%, 95% CI −1.9% to 1.0%).
