FIG 7.
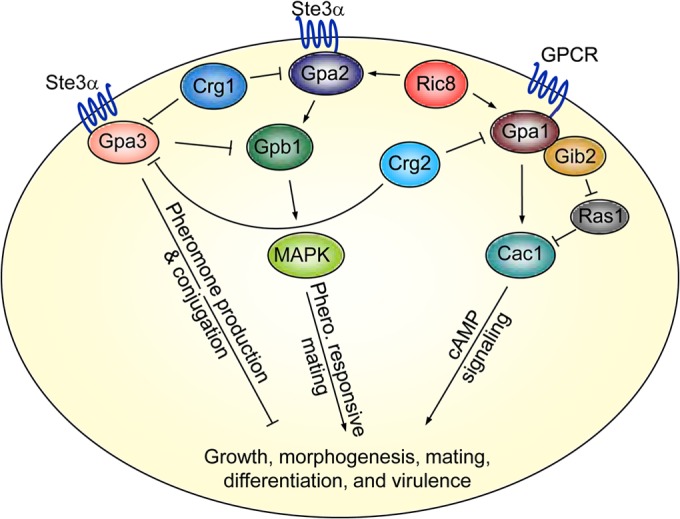
The Ric8 protein regulates the mating and cAMP signal transduction pathways in C. neoformans. The pheromone-responsive mating pathway consists of the upstream components, including the pheromone receptor Ste3α, the RGS protein Crg1, the Gα protein Gpa2, the Gβ protein Gpb1, and either the Gγ protein Gpg1 or the Gγ protein Gpg2. The cAMP signaling pathway consists of the G protein-coupled receptor homolog Gpr4, the Gα protein Gpa1, the Gβ-like protein Gib2, the Gγ proteins Gpg1/Gpg2, and the RGS protein Crg2. Ric8 performs a GEF function toward Gpa1 and Gpa2. It facilitates GDP-to-GTP exchange of Gpa1 to promote cAMP signaling that regulates growth, differentiation, and the production of virulence factors. It also promotes Gpa2 activation to subsequently prolong the positive regulatory function of Gpb1 in mating. Gpa3 likely functions as a distinctive Gα protein in a pathway that senses pheromones but counters the activity of Gpa2. No physical interactions have been established between Gpa3 and Gpb1 or between Gpa3 and Ric8.
