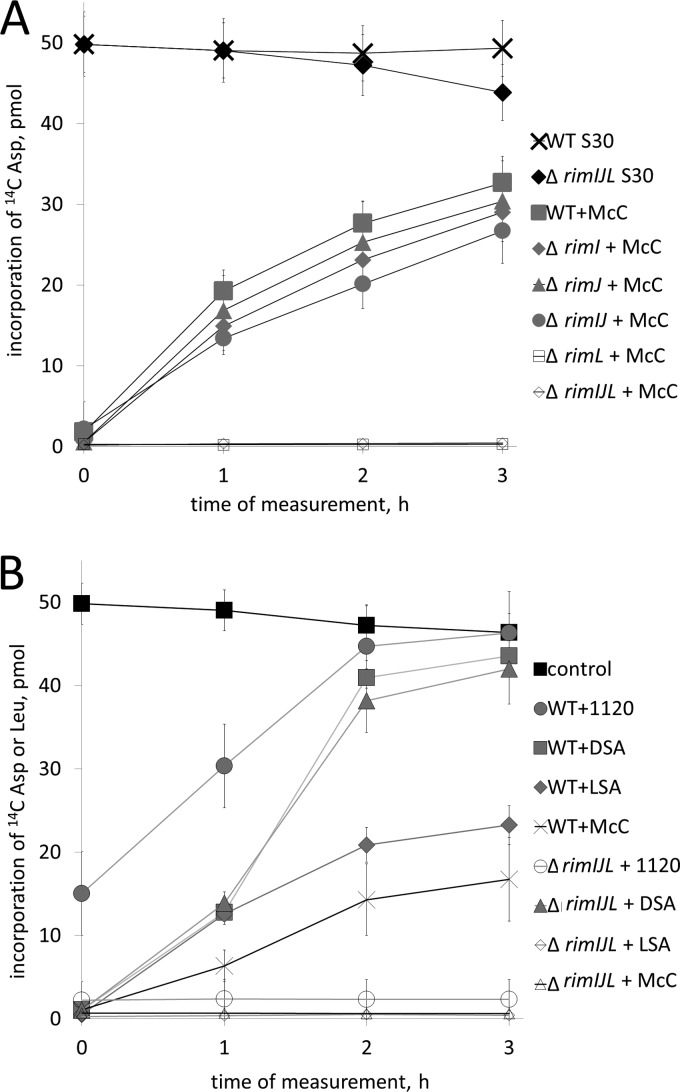
FIG 3.
RimL detoxifies processed McC and LSA in vitro. (A) AspRS-catalyzed aminoacylation of tRNAAsp in S30 extracts prepared from wild-type E. coli and the indicated rim mutants. Extracts were supplied with intact McC and incubated for 15 min to allow processing. Aliquots of extracts were removed, and tRNAAsp aminoacylation reactions were carried out. The first aliquots were removed right after the initial 15-min incubation needed for McC processing. This time point is labeled “0.” The amounts of aminoacylated tRNAAsp (measured as incorporation of [C14] Asp in TCA-precipitable material) are shown. Control shows the time course of aminoacylation levels in wild-type S30 cell extracts without any additions. Data from three independently performed experiments (mean values and standard deviations) are shown. (B) E. coli S30 extracts prepared from wild-type or a triple rim deletion E. coli strain were combined with intact McC, McC(1120), DSA, or LSA. Extracts containing McC or McC(1120) were incubated for 15 min to allow processing before initiating tests for tRNAAsp aminoacylation (times are indicated as indicated for panel A); in extracts containing DSA or LSA, measurements of tRNAAsp or tRNALeu aminoacylation, respectively, were initiated immediately after the addition of inhibitors. Data from three independently performed experiments (mean values and standard deviations) are shown.