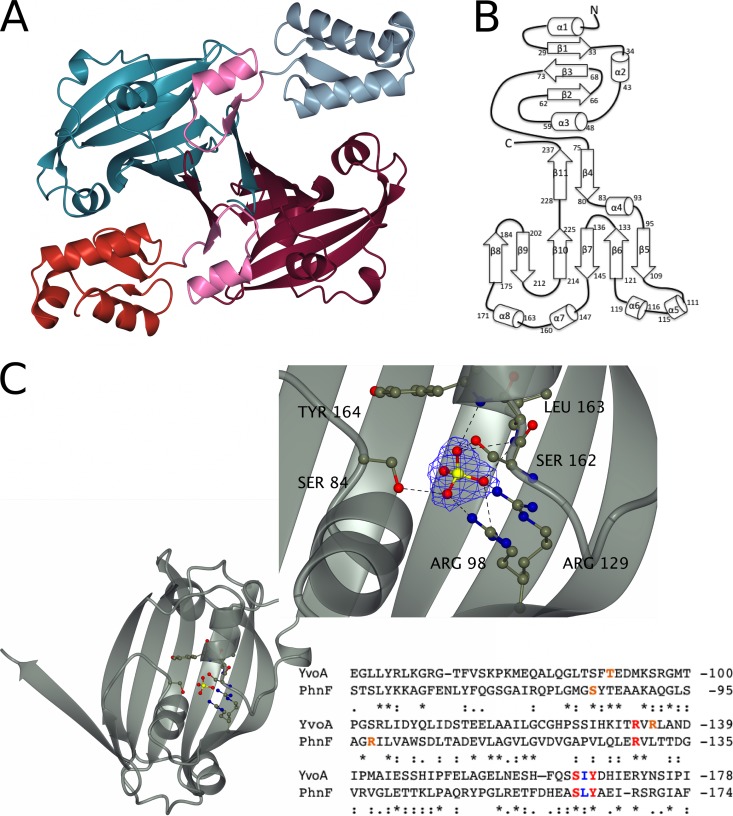
FIG 2.
Key structural features of PhnF from Mycobacterium smegmatis. (A) Crystal structure of the PhnF homodimer. One monomer is shown in gray (N-terminal domain) and cyan (C-terminal domain), and the other monomer is shown in red (N-terminal domain) and purple (C-terminal domain). The linker region of both monomers is shown in pink. (B) Topology plot of the PhnF monomer. (C) Ribbon representation of the effector domain showing the residues involved in SO42− binding in ball-and-stick representation. (Inset) A detailed view of the binding site. Electron density shown is a 2Fo − Fc synthesis contoured at approximately 1σ (0.55 electron/Å2). An alignment of the protein sequences for the C-terminal domains of YvoA and PhnF is shown for comparison. Red, amino acids that form the same contacts with SO42− through their side chains in both proteins; blue, amino acids that form equivalent contacts through their main chains; orange, amino acids that form similar contacts with SO42− but do not occupy similar positions in the binding site. Alignment was performed with the Clustal Omega program (56).