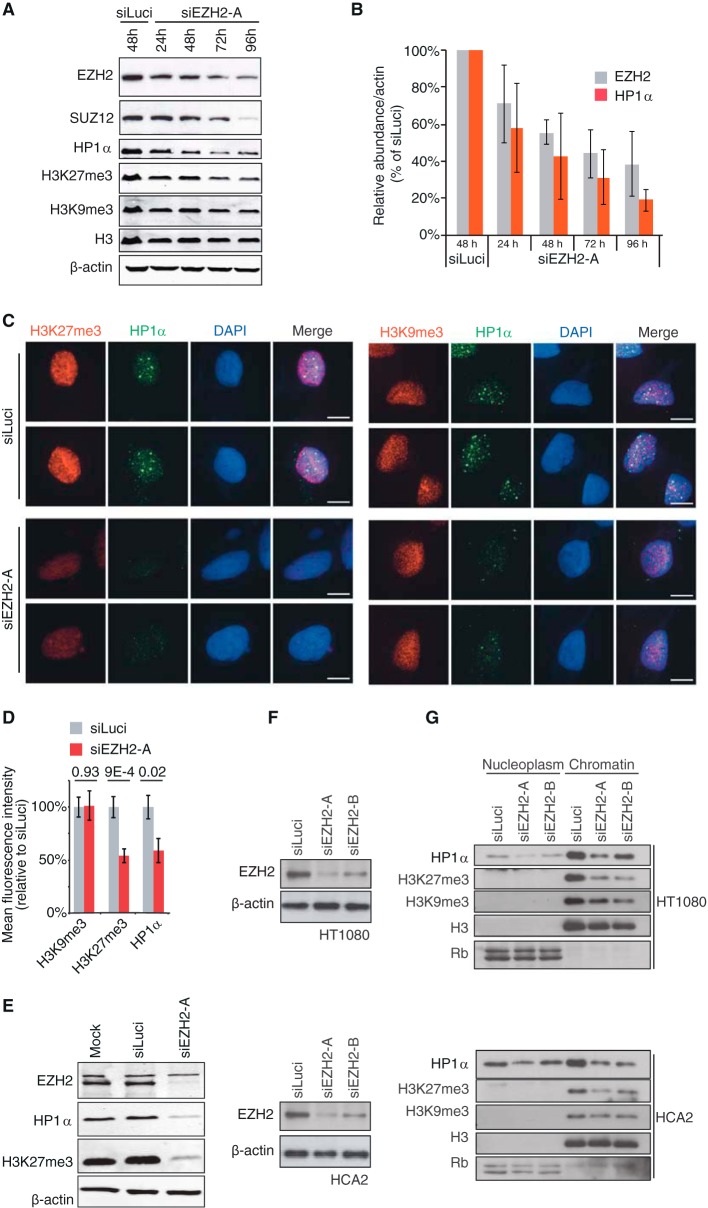
FIG 1.
HP1α dissociates from chromatin and is degraded upon EZH2 depletion. (A) HT1080 cells were treated with siEZH2-A for the indicated time lengths or with siLuciferase (siLuci) for 48 h, and whole-cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with the specified antibodies. (B) Quantification from three independent time course experiments of EZH2 and HP1α protein levels is shown after normalization, first to β-actin and then to siLuci. (C) Immunofluorescence analyses of H3K27me3 and H3K9me3 (red, left and right panels, respectively) and HP1α (green) in Triton-extracted HT1080 cells transfected with siEZH2-A or siLuci for 48 h. Scale bars, 10 μm. (D) Quantification of immunofluorescence shown in panel C on at least 20 nuclei from three independent experiments. Mean fluorescence intensity of nuclei in siEZH2-A-treated cells was compared to that of siLuci control cells. (E) Control for siLuci treatment. HT1080 cells were either mock transfected or treated with siEZH2-A or siLuci for 72 h, and whole-cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with the specified antibodies. (F) Knockdown efficiency of EZH2 in HT1080 (upper panel) or HCA2 (lower panel) cells treated with either siEZH2-A or siEZH2-B. β-Actin is shown as a loading control. (G) Western blot analysis of the nucleoplasm and chromatin fractions from HT1080 (upper panel) or HCA2 (lower panel) cells collected 72 h after transfection with two different siRNAs against EZH2. Membranes were analyzed separately for the presence of HP1α, H3K27me3, and H3K9me3. H3 and Rb levels were used as loading controls for the chromatin and nucleoplasm fractions, respectively. Control cells were transfected with siLuci.