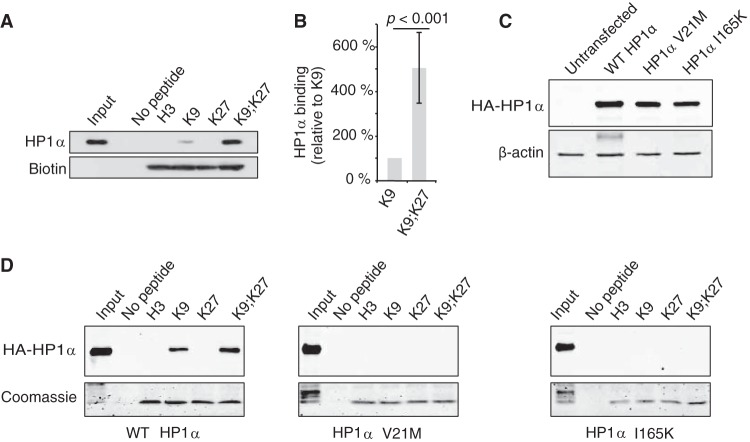
FIG 5.
Binding of human cell extract-derived HP1α to H3 histone tails is increased in the presence of both K9me3 and K27me3 marks. (A) Pulldown experiments with biotinylated H3 tail peptides (H3, unmodified; K9, H3K9me3; K27, H3K27me3; K9;K27, H3K9me3K27me3) and HT1080 cell lysates. After elution, bound HP1α proteins were analyzed by Western blotting and H3 peptides were monitored with HRP-conjugated streptavidin. (B) Quantification of data from panel A from four independent pulldown experiments (n = 4) by normalizing first to the H3 peptide amount and then to HP1α binding to H3K9me3 peptide. (C and D) Both CD and CSD are required for HP1α binding to H3K9me3K27me3 tails. Extracts from HT1080 cells overexpressing either wild-type (WT), V21M, or I165K HA-HP1α proteins (C) were incubated in the presence of immobilized H3 tails as indicated. Bound HA-HP1α and H3 peptides were visualized by, respectively, anti-HA antibodies and Coomassie blue staining (D).