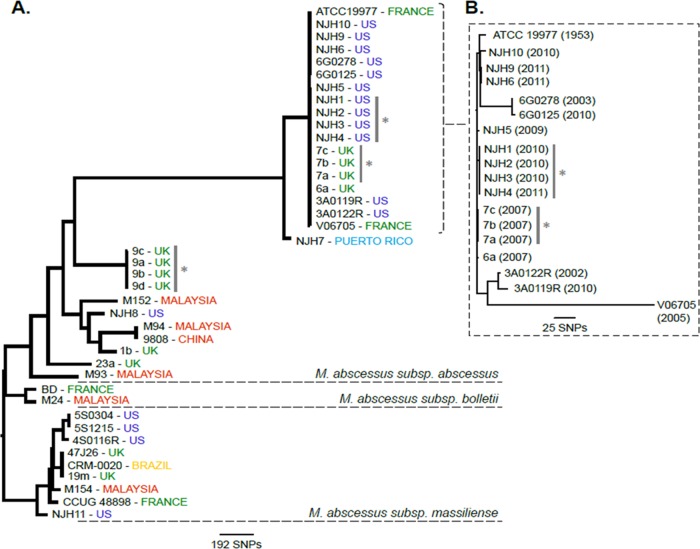
FIG 1.
Phylogenomic comparison of the National Jewish Health (NJH) M. abscessus clinical isolates from the United States, compared with global strains. (A) Genotype data at 2,479 core genome positions, relative to the M. abscessus subsp. abscessus ATCC 19977T reference genome, were used to estimate the phylogeny among 41 M. abscessus isolates using the neighbor-joining algorithm. The phylogenomic tree supports previously recognized subspecies as monophyletic groups. Gray bars and asterisks, isolates acquired from the same patients. (B) Higher-resolution phylogeny of the 18-isolate U.S./European M. abscessus subsp. abscessus cluster was created using genotype information at 128,074 core genome positions. Isolation dates are included. Only 320 (0.25%) of 128,074 core genome sites vary among these isolates.