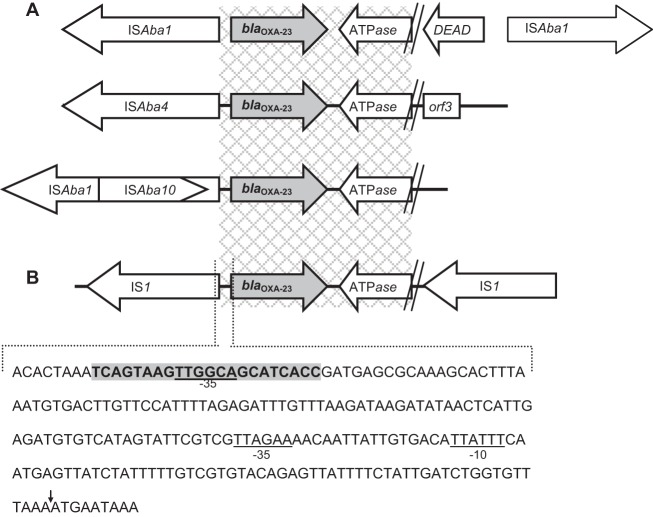
FIG 1.
Schematic representation of the genetic organization of blaOXA-23. (A) In Acinetobacter baumannii, ISAba insertion sequence elements are typically found immediately upstream of blaOXA-23 (8, 9). (B) In the clinical Escherichia coli isolate, blaOXA-23 is flanked by two copies of Enterobacteriaceae insertion sequence IS1. The terminal left inverted repeat (IRL) of IS1 is indicated by the boldface nucleotides with gray shading. The putative −35 promoter of the IRL is underlined and may form hybrid promoters with existing −10 promoters, enabling transcription (11). The ISAba1-associated −35 and −10 promoters are underlined (10). The ATG start codon of OXA-23 is indicated by the vertical arrow (↓). Gray checked regions represent 100% identity between E. coli and A. baumannii. ATPase, gene encoding putative AAA ATPase; DEAD, gene encoding the putative DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) helicase.