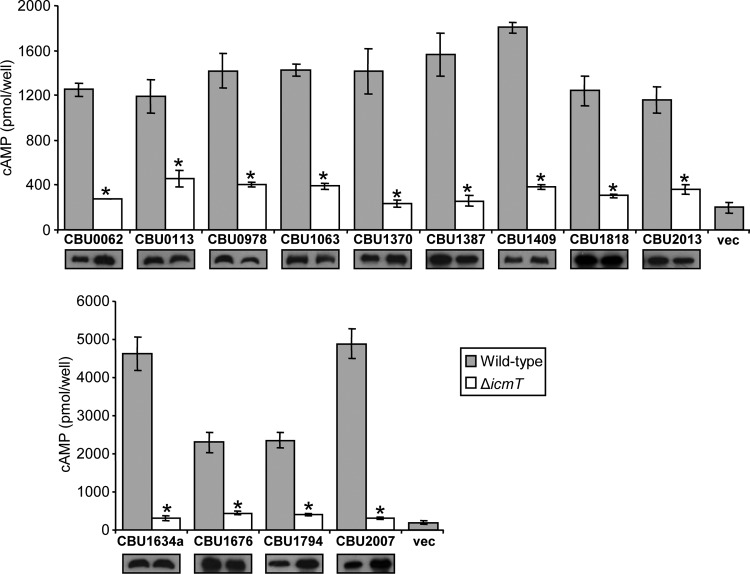
FIG 1.
Icm/Dot-dependent translocation of C. burnetii novel effectors identified by the machine-learning approach. The L. pneumophila wild-type strain JR32 (gray bars) and the icmT deletion mutant GS3011 (white bars) harboring the CyaA fusion proteins (indicated below each bar) were used to infect HL-60-derived human macrophages, and the cAMP levels of the infected cells were determined as described in Materials and Methods. Vector control is indicated as “vec.” The bar heights represent the mean amounts of cAMP per well obtained in at least three independent experiments; error bars indicate standard deviations. The effectors were divided according to the levels of the cAMP obtained in the wild-type L. pneumophila strain. The cAMP levels of each fusion were found to be significantly different (*, P < 0.001, paired Student's t test) between the wild-type strain and the icmT deletion mutant. The C. burnetii novel effectors were examined by Western analysis for their expression in the wild-type strain JR32 (left) and the icmT deletion mutant GS3011 (right) using an anti-CyaA antibody.