FIG 6.
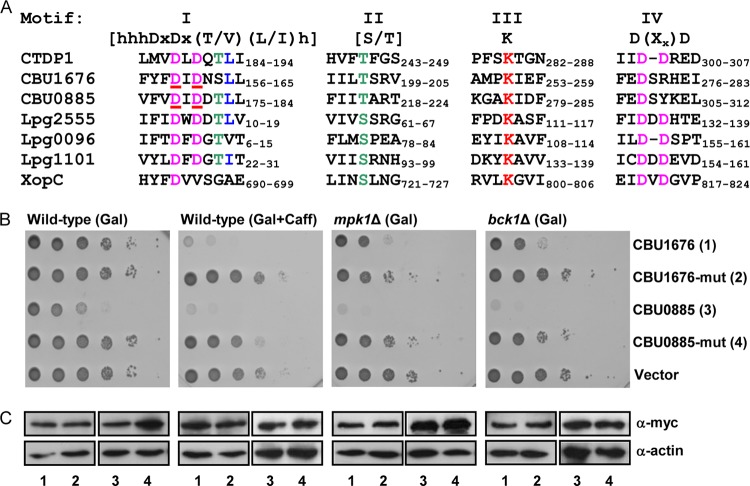
The HAD domain of CBU1676 and CBU0885 is required for their function. (A) Amino acid sequence alignments of HAD motifs I to IV of the human CTDP1 phosphatase; the C. burnetii effectors CBU1676 and CBU0885; the L. pneumophila effectors Lpg2555, Lpg0096, and Lpg1101; and the Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria effector XopC. The highlighted catalytic core residues were previously identified by crystal structure (81). The amino acids that were mutated are underlined in motif I. (B) The yeast growth inhibition of CBU1676 and CBU0885 was eliminated by mutations in their HAD domain. The C. burnetii wild-type and mutated (DID to AIA in residues 178 to 180 of CBU0885 and residues 159 to 161 of CBU1676) effectors were grown on plates containing galactose (Gal) or galactose with caffeine (Gal+Caff) in the wild-type S. cerevisiae BY4741 (Wild-type) and in the mpk1 and bck1 deletion mutants (mpk1Δ and bck1Δ) on plates containing galactose (Gal). pGREG523 (Vector) was used as a negative control. The glucose control plates are presented in Fig. S3 in the supplemental material. (C) The protein levels of the wild-type and mutated myc-tagged effectors were determined by Western blotting using anti-myc antibody. The lanes correspond to those indicated in panel B. Actin was used as a loading control.