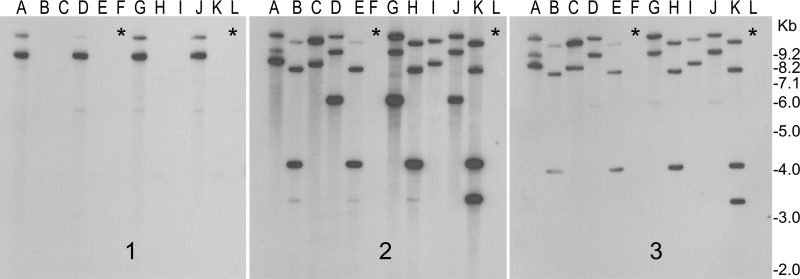
FIG 2.
RS1ϕ-induced elimination of CTX prophage from toxigenic V. cholerae. Toxigenic strains were exposed to RS1-Kmϕ and screened for the production of CTX-negative derivatives (see the text for details). DNAs isolated from representative colonies were digested with BglI and analyzed by Southern blotting with probes for the ctxAB (1), rstR (2), and rstC (3) genes. Lanes A, P27457 wild type; lanes B and C, P27457 infected with RS1-Kmϕ; lanes D, G7555 wild type; lanes E and F, G7555 infected with RS1-Kmϕ; lanes G, strain G3985 wild type; lanes H and I, G3985 infected with RS1-KmΦ; lanes J, Syria-3 wild type; lanes K and L, Syria-3 infected with RS1-KmΦ. Lanes marked with asterisks show CTX-negative derivatives which simultaneously lost RS1 and, hence, all rstR- and rstC-hybridizing sequences.