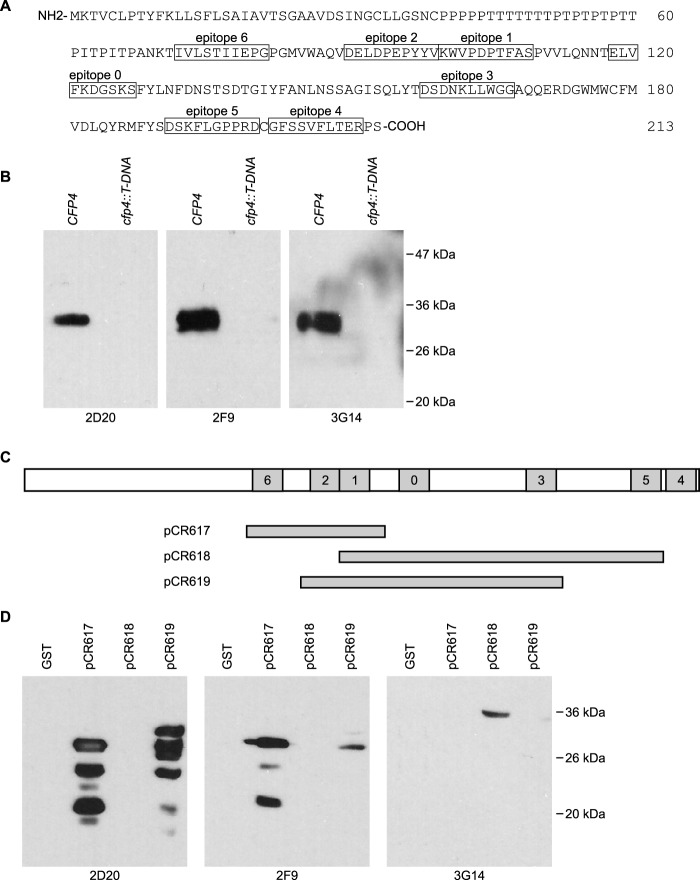
FIG 2.
Mapping of epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies to Cfp4. (A) Primary amino acid sequence of the Cfp4 protein showing the location of the epitopes used (boxed amino acids) for immunization of mice (epitopes 0 to 6). (B) Specificity of Cfp4 recognition by monoclonal antibodies as demonstrated by immunoblots of Histoplasma culture filtrates from Cfp4-producing and Cfp4-lacking yeasts. Culture filtrates were collected from Cfp4-producing (CFP4; strain OSU45) and cfp4 mutant yeasts (cfp4::T-DNA; strain OSU84). PNGase F-treated samples were immunoblotted with hybridoma supernatants 2D20, 2F9, and 3G14. (C) Schematic of the Cfp4 protein and the constructs used to map the recognized Cfp4 epitopes. Shaded boxes represent epitopes 0 to 6, and horizontal bars below show the Cfp4 fragments produced in E. coli as fusions to glutathione S-transferase (GST) from plasmids pCR617, pCR618, and pCR619. (D) Delineation of the epitopes recognized by each monoclonal antibody. Crude E. coli lysates from GST-expressing or GST::Cfp4 fusion-expressing bacteria were immunoblotted with hybridoma supernatants.