FIG 3.
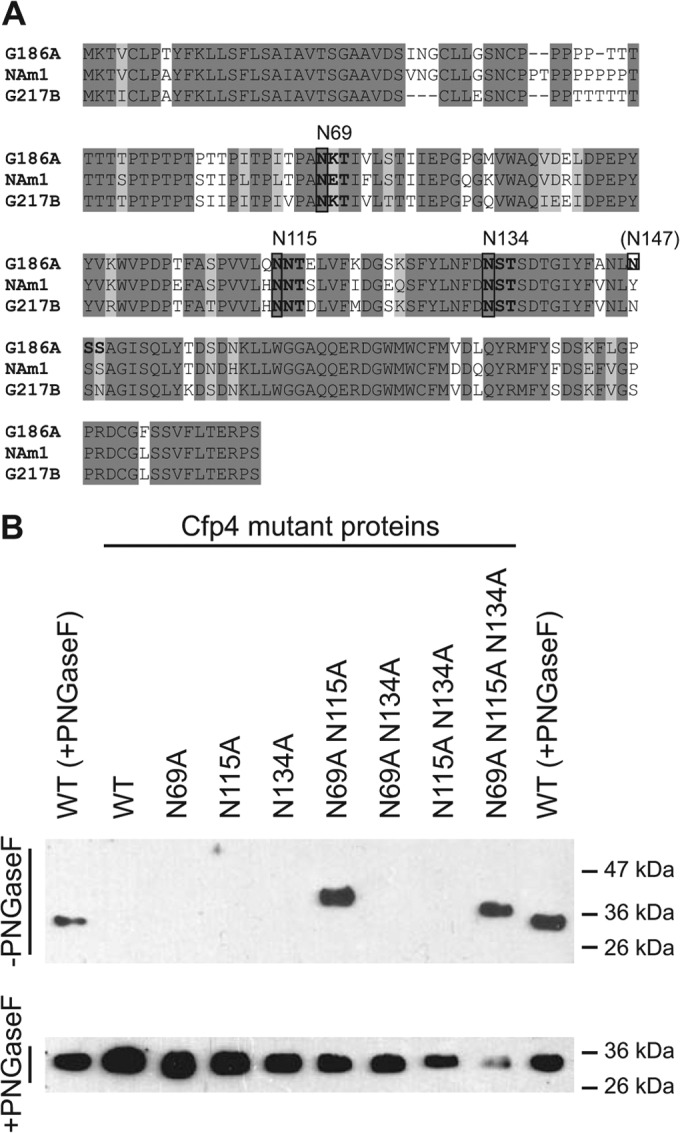
Identification of N-linked glycosylation modification sites on Cfp4. (A) Amino acid sequence of Cfp4 from three phylogenetic groups of Histoplasma indicating sites of potential N-linked glycosylation. Shading of amino acids represents completely conserved residues (dark shading) or conservation in 2 of 3 lineages (light shading). Consensus N-linked glycosylation sequons (Asn-X-Ser/Thr) are indicated in bold, with the corresponding asparagine residue above the sequence. (B) Delineation of N-linked glycosylation sites on Cfp4 through mutation of candidate sites. Culture filtrates from Histoplasma yeasts expressing mutant Cfp4 proteins (strains OSU217 to OSU226) were immunoblotted using the 2D20 antibody. Culture filtrate proteins were electrophoresed without prior treatment with PNGase F (−PNGaseF; top) or with PNGase F treatment (+PNGaseF; bottom). The leftmost and rightmost lanes in both panels contained PNGase F-treated culture filtrate proteins from the wild type [WT (+PNGaseF); G186A strain]. Labels above the panels indicate which specific asparagines were mutated to alanines in the mutant proteins.
