FIG 4.
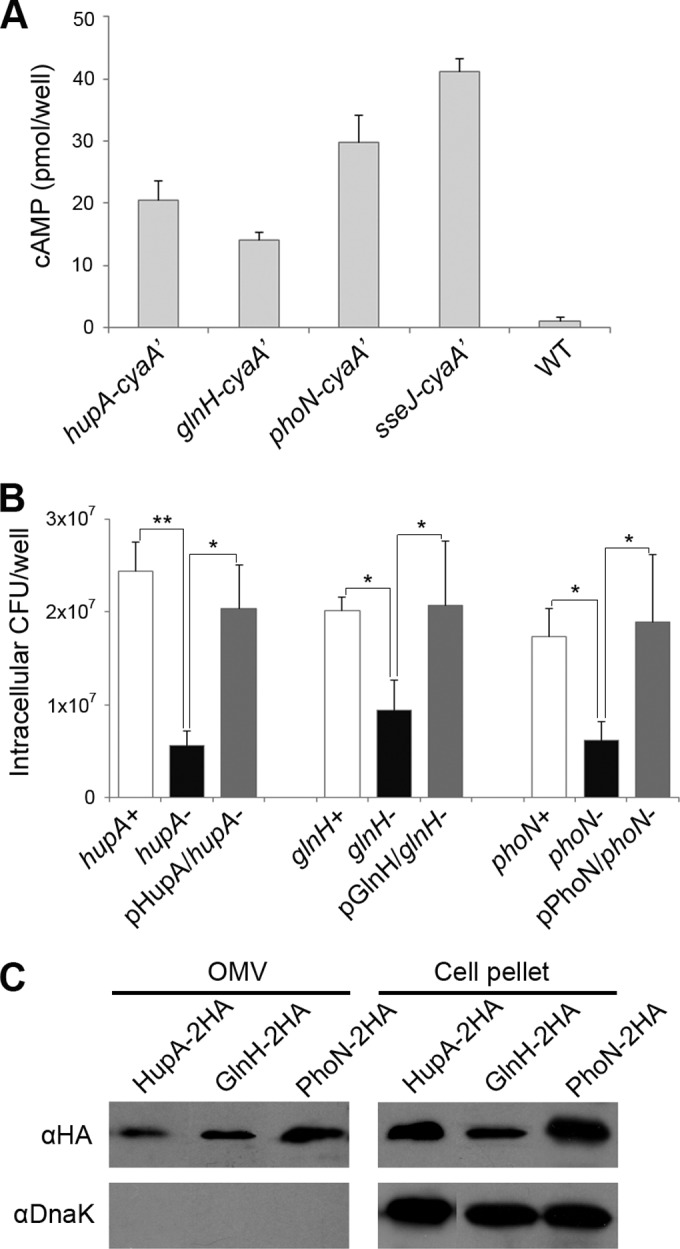
OMV-associated virulence proteins translocated into the macrophage cytoplasm. (A) Translocation of HupA, GlnH, and PhoN into the host cytosol. HupA, GlnH, and PhoN were tagged with CyaA′ at their C termini using genetic modification as described in Materials and Methods. Macrophages were infected with Salmonella strains producing CyaA′-tagged proteins for 12 h, and the intracellular cAMP levels were assayed to test the translocation of the CyaA′-tagged proteins into the host cytoplasm. SseJ, a well-known SPI-2 T3SS-secreted effector, was also tagged with CyaA′ and examined with three tested proteins. The intracellular cAMP levels averaged from three separate experiments are shown with their standard deviations. One-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc analysis were used for the statistics (P < 0.05). (B) Intracellular survival assay of ΔhupA, ΔglnH, and ΔphoN mutants. Macrophages were infected with Salmonella strains lacking HupA, GlnH, or PhoN, and the intracellular CFU were enumerated at 12 h postinfection. To complement the attenuated survival of the deletion strains, plasmids expressing HupA, GlnH, or PhoN were introduced into the mutant strains lacking the corresponding functional alleles. The averages and standard deviations of the results from three independent infections are shown. The asterisks indicate a significant difference, as determined by ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005. (C) Immunoblot verification of OMV localization of HupA, GlnH, and PhoN. Salmonella strains producing HupA, GlnH, and PhoN tagged with HA were cultivated under acidic MgM conditions, and the OMVs were isolated. The OMV fractions and whole-cell lysates were analyzed through an immunoblot assay with an anti-HA antibody to verify the presence of HupA, GlnH, and PhoN in the OMVs. The presence of DnaK was also examined to evaluate the purity of the OMV fractions.
