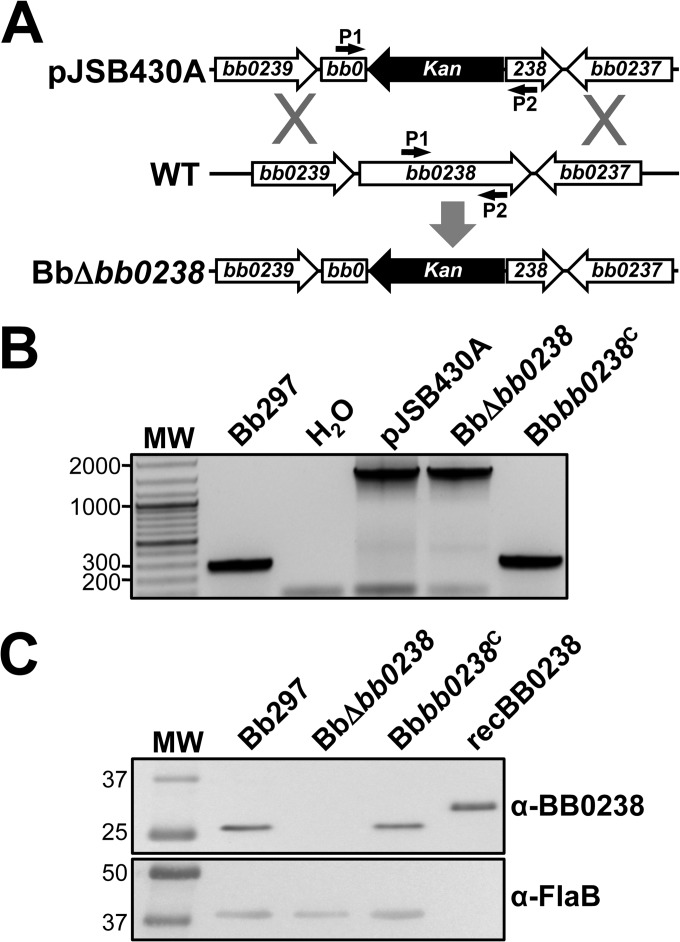
FIG 1.
Generation and confirmation of BbΔbb0238 and the Bbbb0238C complemented clone. (A) Diagram illustrating the approach to inactivating bb0238 in Bb297. pJSB430A, relevant region of the bb0238::Kan mutagenesis construct; WT, bb0238 and flanking regions from the B. burgdorferi chromosome; BbΔbb0238, genomic arrangement of the bb0238::Kan mutant. The small arrows denote the relative positions of the bb0238 P1 and P2 diagnostic primer pair. (B) PCR confirmation of the BbΔbb0238 mutant and complemented Bbbb0238C. PCR with primers P1 and P2 results in different amplicon sizes, 287 bp (wild type) and 1,475 kb (bb0238::Kan). Bb297, wild-type B. burgdorferi; H2O, negative control for amplification; pJSB430A, bb0238::Kan suicide vector used to interrupt bb0238. DNA size standards (lane MW), indicated on the left, are shown in kilobases. (C) Immunoblot analysis of BB0238 and FlaB in Bb297, BbΔbb0238, and Bbbb0238C. Antibodies used to detect the respective proteins are indicated on the right. recBB0238 denotes the lane containing His6-tagged BB0238 recombinant protein used to generate antisera. The relevant molecular masses (kDa) of the standard (lane MW) are shown on the left.