FIG 7.
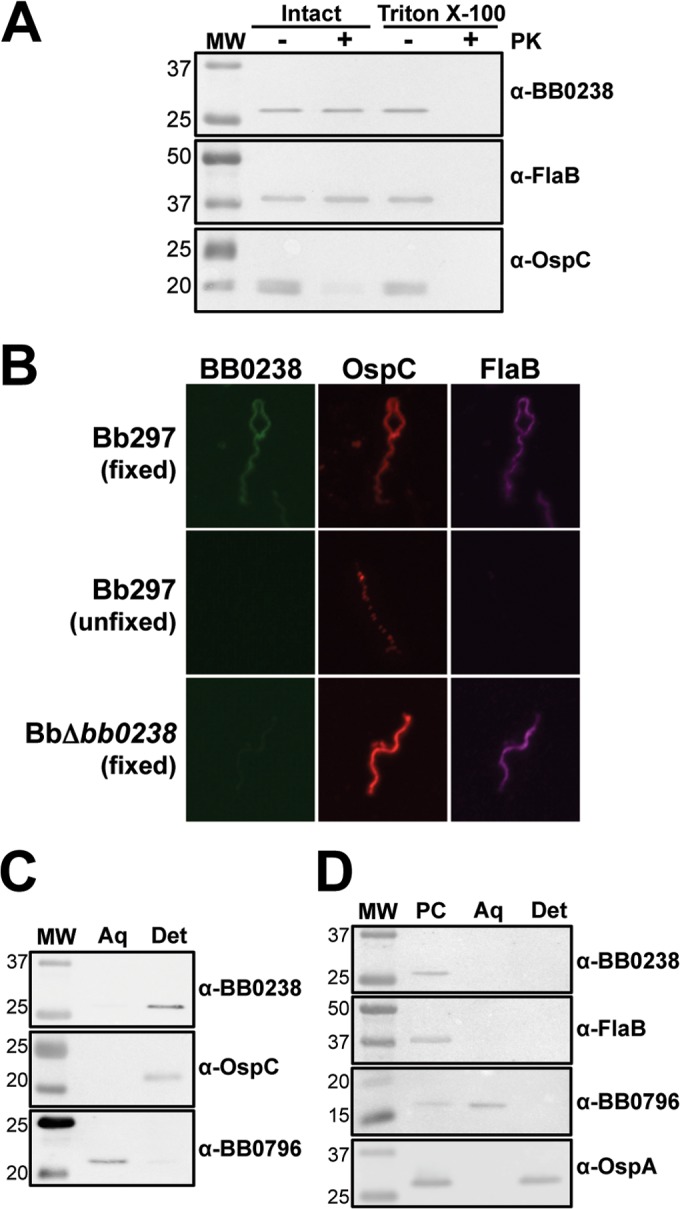
Cellular localization of BB0238. (A) Immunoblot analysis of the proteinase K accessibility assay. Bb297 cells were incubated with or without proteinase K (PK) in the presence or absence of Triton X-100. Antibodies to detect the respective proteins are listed on the right, and the relevant molecular masses (lane MW) are shown on the left in kDa. FlaB, negative control; OspC, positive control. (B) IFA of Bb297 and BbΔbb0238. Fixed, cells were fixed to glass slides by air drying, heated, and then incubated in acetone; the slides were blocked and incubated with primary antibody and then secondary antibody. Unfixed, cells were incubated with primary antibody and then washed and fixed to glass slides with formaldehyde; the slides were then incubated with secondary antibody. Secondary antibodies for detection of BB0238, OspA, and FlaB were anti-rat Alexa Fluor 488, anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 594, and anti-chicken Alexa Fluor 647, respectively. (C) Immunoblot analysis of whole-cell phase partitioning. Bb297 cells were phase separated into aqueous (Aq) and detergent (Det) fractions. Antibodies to detect the respective proteins are listed on the right, and the relevant molecular masses (lane MW) are shown on the left in kDa. OspC was used as a control for the membrane-localized, detergent-enriched fraction, and detection of BB0796 was used as an aqueous control. (D) Immunoblot analysis of cellular fractionation. Bb297 cells were incubated with Triton X-114. The protoplasmic cylinder (PC) was pelleted, and samples were incubated at 37°C for phase separation. The aqueous (Aq) and detergent (Det) fractions were then separated. Antibodies to detect the respective proteins are listed on the right, and the relevant molecular masses (lane MW) are shown on the left in kDa. FlaB was used as a protoplasmic cylinder control, periplasmic BB0796 as an aqueous control, and outer-membrane-localized OspA as a detergent control. The data shown are representative blots from a minimum of two independent experiments.
