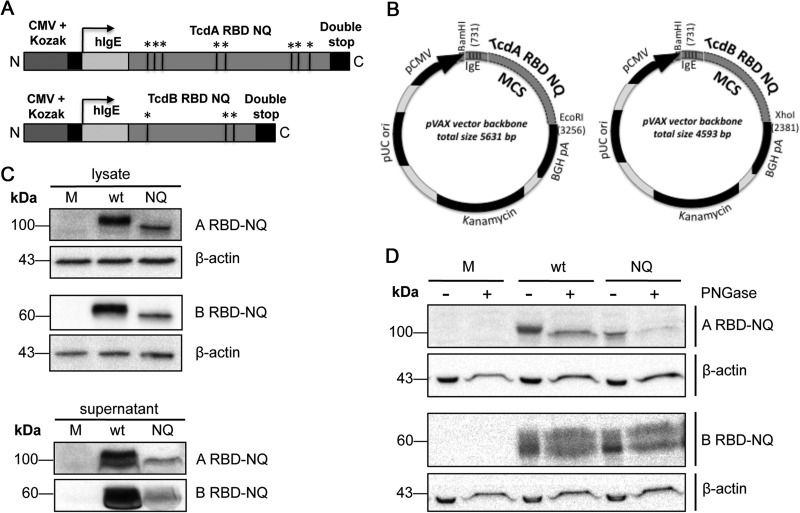
FIG 1.
Construction and expression of a DNA vaccine encoding the RBDs from TcdA and TcdB. (A) ARBD-NQ and BRBD-NQ constructs contain a cytomegalovirus promoter with a Kozak sequence, a human IgE leader, and either the TcdA RBD or TcdB RBD followed by two stop codons. Within the RBD sequence, the black lines indicate putative N-linked glycosylation sites that were altered. Black lines and asterisks refer to putative N-linked glycosylation sites. (B) The inserts were cloned into pVAX1, creating four plasmids: pARBD-wt, pARBD-NQ, pBRBD-wt, and pBRBD-NQ. MCS, multiple cloning site. (C) pARBD-NQ and pBRBD-NQ expression was confirmed in transfected HEK-293T cells. Forty-eight hours after transfection, immunodetection of RBD protein was performed on the lysates (30 μg) and supernatants (100 μg for TcdA RBD and 150 μg for TcdB RBD) using mouse RBD antiserum. (D) Similar amounts of lysates and supernatants were treated with PNGase F and subjected to SDS-PAGE in order to assess the glycosylation of RBD proteins in vitro. M, mock.